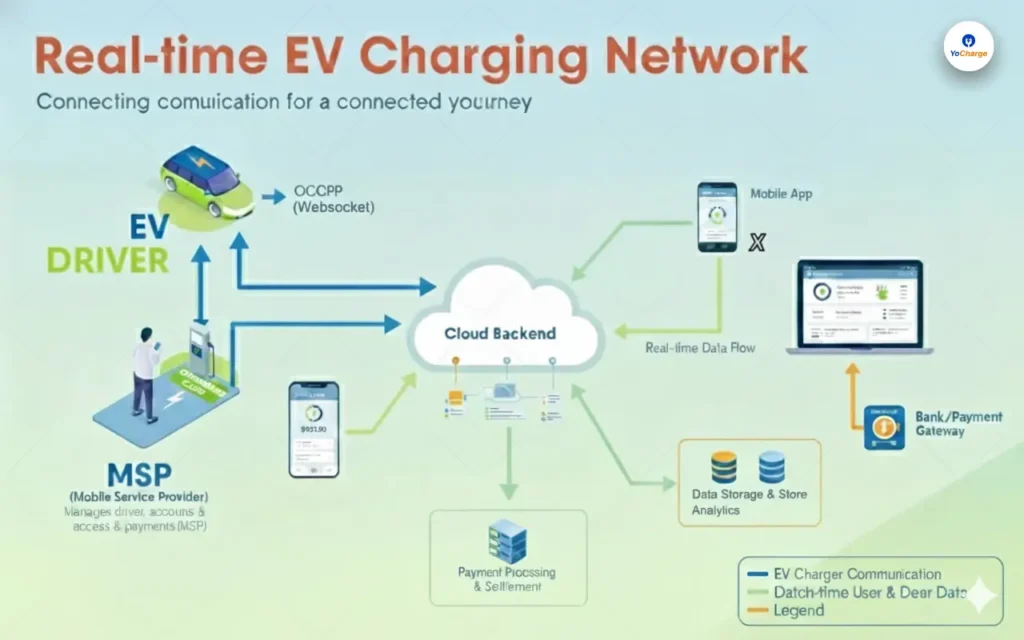
Electric Mobility is revolutionary transforming the way we move & the energy sources we rely on for transportation. At the heart of this transformation lie open protocols, a crucial but often overlooked aspect of e-mobility. Open protocols in e-mobility play a crucial role in fostering a connected and accessible electric vehicle ecosystem. They enable different stakeholders, including EV manufacturers, charging station operators, and service providers, to work together harmoniously, promoting the growth and sustainability of e-mobility on a global scale.
In this article, we will introduce you to the world of open protocols in e-mobility, exploring their importance, common types, benefits, challenges, and their role in shaping the future of sustainable transportation.
What is e-mobility ?
E-mobility, short for electric mobility, refers to the use of electric power to propel vehicles, ranging from electric cars and bikes to buses and scooters. This shift towards electric vehicles is driven by the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, combat climate change, and improve air quality in urban areas. E-mobility not only helps in achieving these environmental goals but also promises lower operating costs and increased energy efficiency.
Common Open Protocols in electric mobility
“Open Protocols” refers to standardized sets of rules and communication methods that enable different components of the electric vehicle (EV) ecosystem to interact and exchange data effectively. They are the language that allows various components of the EV ecosystem to communicate seamlessly, ensuring efficient and reliable charging processes.
Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP):
OCPP is one of the most widely used protocols for communication between charging stations and central management systems. It defines a set of rules that govern the interaction between charging points and cloud based charging management platform, allowing for flexibility and compatibility between charging stations of different manufacturers.
Open Charge Point Interface (OCPI):
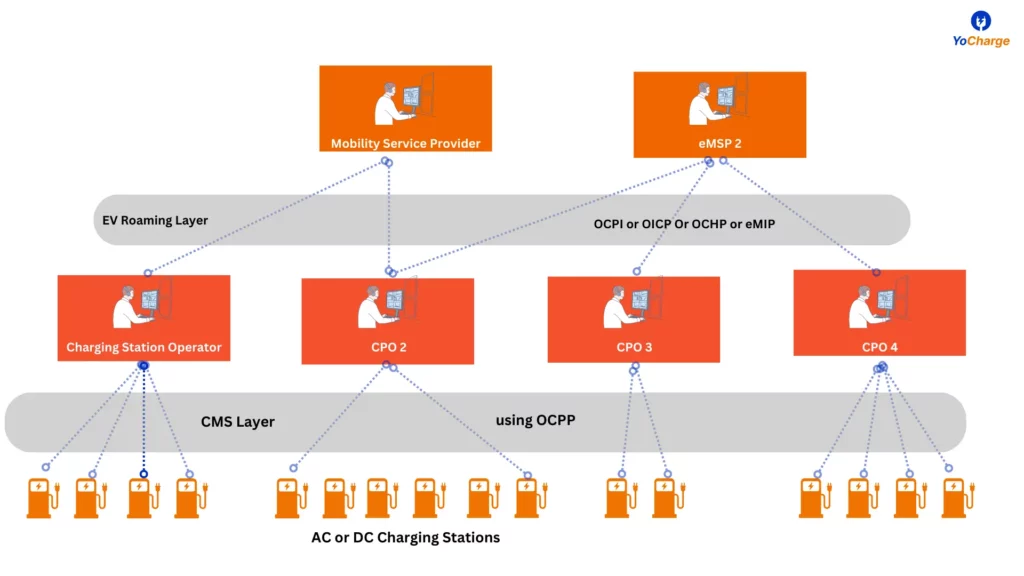
OCPI is another important open protocol that facilitates communication between charging station operators and e-mobility service providers. It streamlines processes like billing and real-time data sharing, ensuring a smooth user experience. The OCPI protocol is managed and maintained by the EVRoaming Foundation, ensuring its free availability.
Open InterCharge Protocol (OICP):
OICP is a protocol that focuses on interoperability between different e-mobility service providers. It standardizes communication between charging networks, promoting seamless roaming for EV users, regardless of their service provider. The Open Intercharge Protocol (OICP) has been developed by Hubject, a group of German automotive and energy companies, in 2012.
Open Clearing House Protocol (OCHP):
OCHP plays a pivotal role in creating a clearinghouse for charging data. It enables different charging station operators to share data securely and efficiently, improving transparency and reliability in the e-mobility ecosystem.
eMobility Inter-operation Protocol (eMIP):
MIP is an EV roaming protocol that enables communication between MSPs and CPOs via a roaming hub. eMIP is a protocol designed to facilitate cross-border charging. It ensures that EV drivers can access charging infrastructure in different countries without facing compatibility issues or excessive fees.
Also Read
The different EV Roaming Protocols – OCPI, OICP, OCHP, eMIP
Open Smart Charging Protocol (OSCP)
Open Smart Charging Protocol (OSCP) is an open communication protocol between a charge point management system and an energy management system. OSCP empowers charging stations to dynamically adapt charging rates based on factors like grid demand, energy prices, and user preferences, optimizing the charging process for efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Open ADR
OpenADR is an open, secure, and two-way information exchange model facilitating automated demand response (DR) actions that help balance grid supply and demand or mitigate high electricity costs. It establishes a standardized method for communication between utility companies and charging systems. OpenADR enables utilities to send signals to EV charging stations, directing them to adjust charging rates based on grid conditions, demand fluctuations, and price signals. This protocol promotes grid stability, minimizes energy costs for EV owners, and supports the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid
ISO 15118:
ISO 15118 is an international standard that covers the communication between EVs and charging infrastructure. It enables secure, automated, and bi-directional communication, allowing EVs to negotiate charging parameters with the charging station, optimizing charging processes. Read more
Benefits of Using Open Protocols:
Open protocols define a common language or framework that allows different entities within the e-mobility ecosystem to communicate seamlessly. This communication can involve tasks like authorizing charging sessions, transmitting charging rates, providing real-time status updates, and facilitating payment transactions. The major benefits of using Open Protocols include:
Interoperability:
One of the primary benefits of open protocols is interoperability. They break down the barriers between different charging stations, service providers, and EVs, allowing users to charge their vehicles seamlessly, regardless of their location or service provider.
Reduced Operating Costs:
Open protocols promote healthy competition and prevent vendor lock-in, leading to cost-effective solutions for e-mobility stakeholders. This cost efficiency ultimately benefits EV drivers and accelerates the adoption of electric vehicles.
Scalability:
As the e-mobility ecosystem continues to expand, open protocols provide the scalability required to accommodate the growing number of EVs and charging stations. This adaptability ensures that the infrastructure can keep pace with the increasing demand.
Future-Proofing:
Open protocols are designed to evolve with the changing landscape of e-mobility. They can incorporate new features and technologies, ensuring that the infrastructure remains relevant and future-proof.
In conclusion, open protocols in e-mobility play a crucial role in fostering a connected and accessible electric vehicle ecosystem. It enables different stakeholders like EV companies, CPO’s to work together harmoniously and promote e-mobility on a global scale.