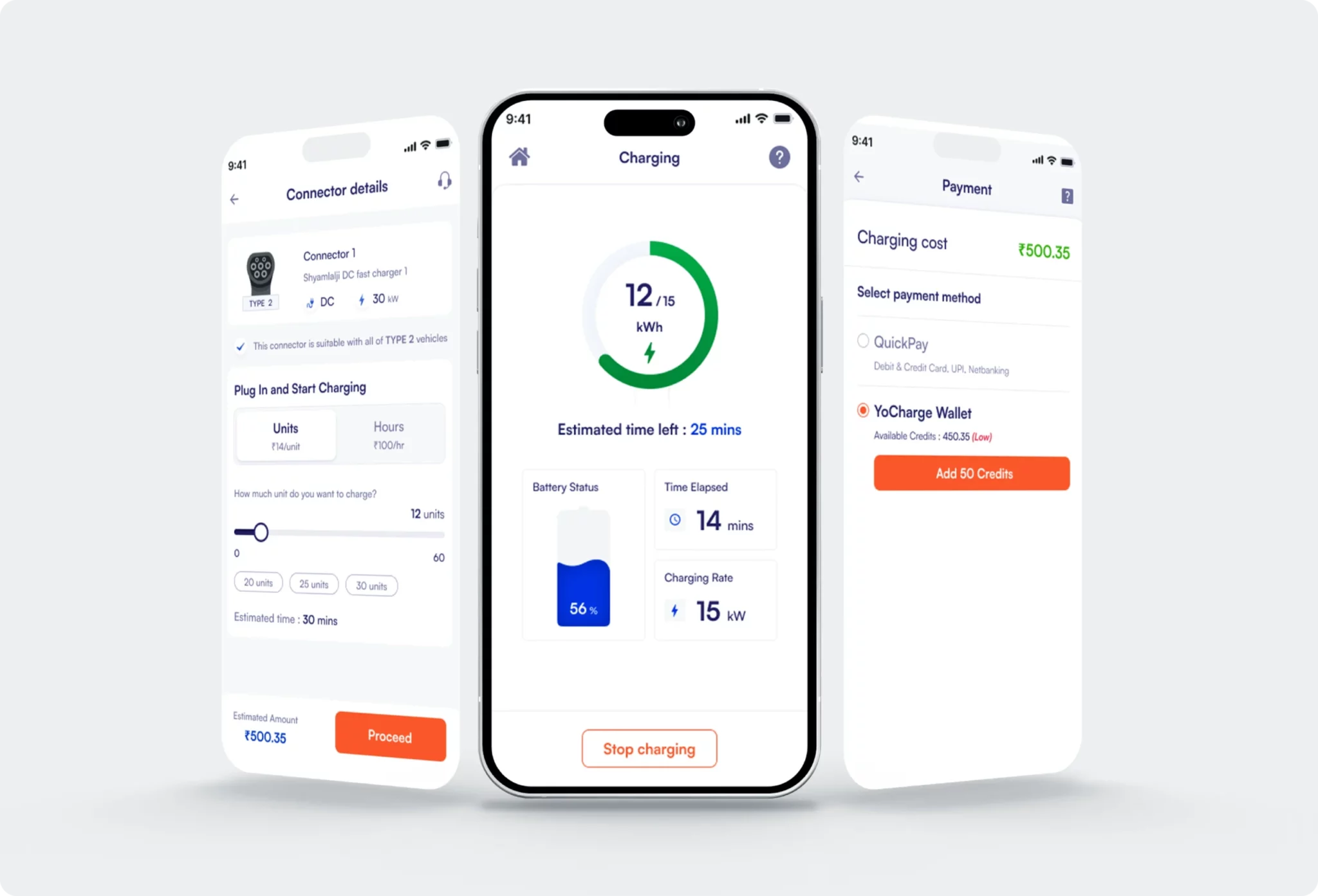
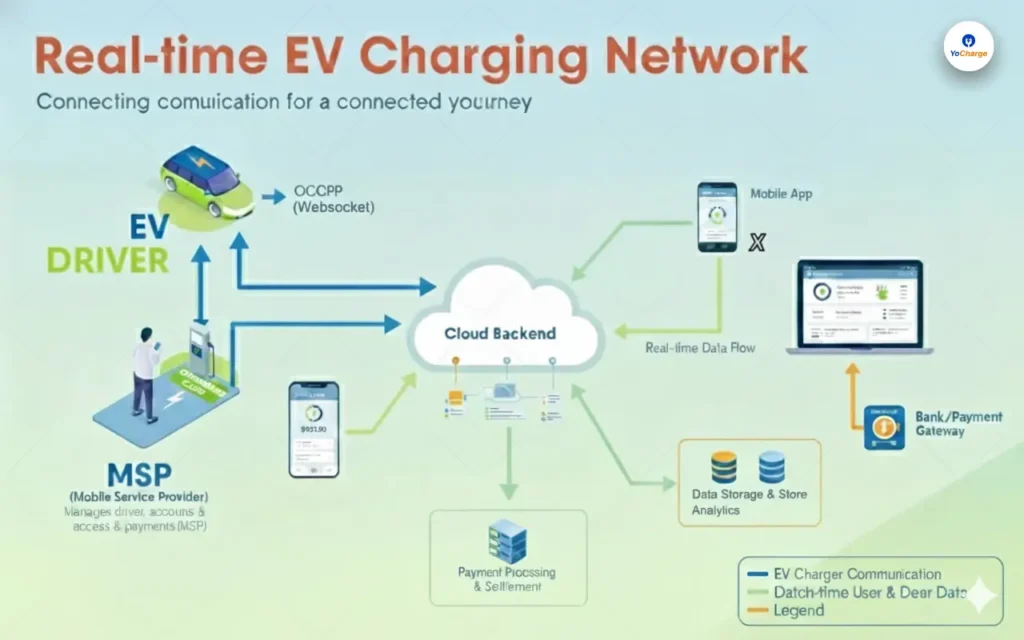
The transportation sector is a major contributor to global climate change, accounting for roughly a quarter of greenhouse gas emissions worldwide. In response, electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining significant traction as a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
Better technology, cheaper batteries, and environmental worries are driving the rise of electric cars. Sales of EVs reached a record high of 6.6 million in 2021, representing a rapid increase from the past years. This trend is expected to continue, with forecasts predicting that EVs could account for over half of all new car sales globally by 2030 in the USA.
However, the successful transition to widespread adoption of EVs hinges on a crucial factor: the role of power utilities. These entities are uniquely positioned to enable this transition by building and maintaining a robust charging infrastructure, managing and upgrading the electricity grid, and educating consumers about the benefits of EVs.
Key Contributions Of Power Utilities In EV Industry
Building Charging Infrastructure
The widespread adoption of EVs relies heavily on a robust and accessible charging infrastructure. This network of charging stations allows drivers to conveniently replenish their vehicle’s battery, addressing a major concern known as range anxiety (fear of running out of power before reaching a charging point.)
Power utilities can play a critical role in facilitating the installation of charging stations in various locations, including:
- Homes: Enable homeowners to install personal charging stations in their garages or driveways for overnight charging.
- Workplaces: Collaborating with businesses to install charging stations in parking lots, encouraging employees to switch to EVs.
- Public Locations: Participating in the development of charging networks along highways, in public parking areas, and at shopping centers, ensuring convenient charging options for long-distance travel and everyday errands.
It is important to note that different types of charging stations offer varying charging speeds and functionalities:
- Level 2 Chargers: These are commonly found in public locations and workplaces, providing faster charging than a standard household outlet.
- DC Fast Chargers: Offering the most rapid charging option, typically found along highways, allowing drivers to significantly replenish their battery in a short time, ideal for long journeys.

Grid Management And Upgradation
The increasing demand for EV charging will undoubtedly impact the electricity grid. Utilities need to be prepared to manage this growing energy demand efficiently and reliably. Here is how they can achieve this:
Smart Grid Technologies
Implementing real-time monitoring and control systems allows utilities to gain a better understanding of electricity usage patterns and optimize energy distribution. This can improve grid efficiency and ensure stable power supply during peak charging periods.
Grid Modernization
Upgrading existing infrastructure, including substations, transformers, and distribution networks, is crucial to handle the higher power demands associated with widespread EV adoption. This ensures the grid can effectively transmit and distribute the additional electricity required for charging millions of EVs.
Demand-Side Management
To help the grid during busy times, we can ask people to charge their electric cars when demand is low. We can give discounts for charging at night or on weekends to encourage this behavior as charging at off-peak hours can ease pressure on the grid. By using dynamic pricing and incentives, we can motivate consumers to charge their EVs when demand is lower.

Consumer Education And Engagement
Building public trust and encouraging consumer adoption of EVs requires extensive education and engagement. Power utilities can play a crucial role in this process by:
- Educating Consumers about the benefits of EVs, including environmental advantages, cost savings on fuel and maintenance compared to gasoline vehicles, and the availability of different charging options.
- Collaborating With Other Stakeholders, such as government agencies, auto manufacturers, and non-profit organizations, to develop and distribute educational resources and workshops.
- Offering Financial Incentives can significantly encourage the transition to EVs. Utilities can work with governments and other stakeholders to provide subsidies for EV purchases and charging infrastructure installation at homes and businesses.
Suggested Reads: How Can Power Utilities Prepare For The EV Industry Expansion?
Benefits Of Power Utilities In The EV Industry
Sustainable Growth And Environmental Benefits
The widespread adoption of EVs and a robust charging infrastructure offer significant environmental advantages:
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, contributing directly to combating climate change. A study by the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT) found that switching from gasoline to electric vehicles can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation sector.
Improved Air Quality
Since EVs do not emit harmful pollutants like nitrogen oxides and particulate matter, their widespread adoption can lead to cleaner air. A study by the American Lung Association found that transitioning to EVs could significantly reduce air pollution and improve public health.
Promoting Renewable Energy Integration
As the demand for electricity increases with more EVs on the road, utilities have an opportunity to integrate more renewable energy sources like solar and wind power into the grid. This can further amplify the environmental benefits of EVs by reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Economic Opportunities And Innovation Benefits
The transition to EVs and the development of a robust charging infrastructure presents exciting economic opportunities:
- New Job Creation: The widespread adoption of EVs is expected to generate new jobs in various sectors, including:
- Charging Station Installation And Maintenance: As the number of charging stations grows, skilled labor will be needed for installation, repair, and upkeep.
- Smart Grid Technology Development And Deployment: Upgrading and modernizing the grid to handle increased EV charging demand will require the expertise of engineers and technicians specializing in smart grid technologies.
- Renewable Energy Generation: The increased demand for electricity to power EVs can drive the growth of the renewable energy sector, creating jobs in areas like solar panel and wind turbine manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
- Fostering Innovation: Utility involvement in the EV industry can stimulate innovation across various sectors. They can collaborate with research institutions and technology companies to develop:
- Next-Generation Charging Technologies: This could include faster charging options, smarter charging solutions that optimize grid usage, and improved battery technology for longer range and shorter charging times.
- Advanced Grid Management Systems: Developing intelligent systems that can effectively manage peak demand periods and integrate renewable energy sources into the grid efficiently.
Suggested Reads: Indian Standards for Electrotechnology in Mobility 2024
The Final Words
In conclusion, the significance of power utilities in propelling the expansion of the EV industry cannot be overstated. As demand for electric vehicles continues to rise, power utilities play a crucial role in ensuring the infrastructure necessary for their widespread adoption is in place. From developing efficient charging networks to integrating renewable energy sources, power utilities are at the forefront of driving this transformative change.
Join the movement and be part of shaping the future of transportation with YoCharge. Together, we can drive positive change and accelerate the transition to electric mobility.