Picture this: You are on a long road trip, and your electric vehicle needs a recharge. Instead of waiting hours, you are back on the road in just 20 minutes. This is not science fiction; it is the reality made possible by fast EV charging technology.
As electric vehicles take over the roads, the demand for faster, more efficient charging solutions is skyrocketing. In this article, we will learn about Fast EV Charging Technology, its benefits, challenges, and types.
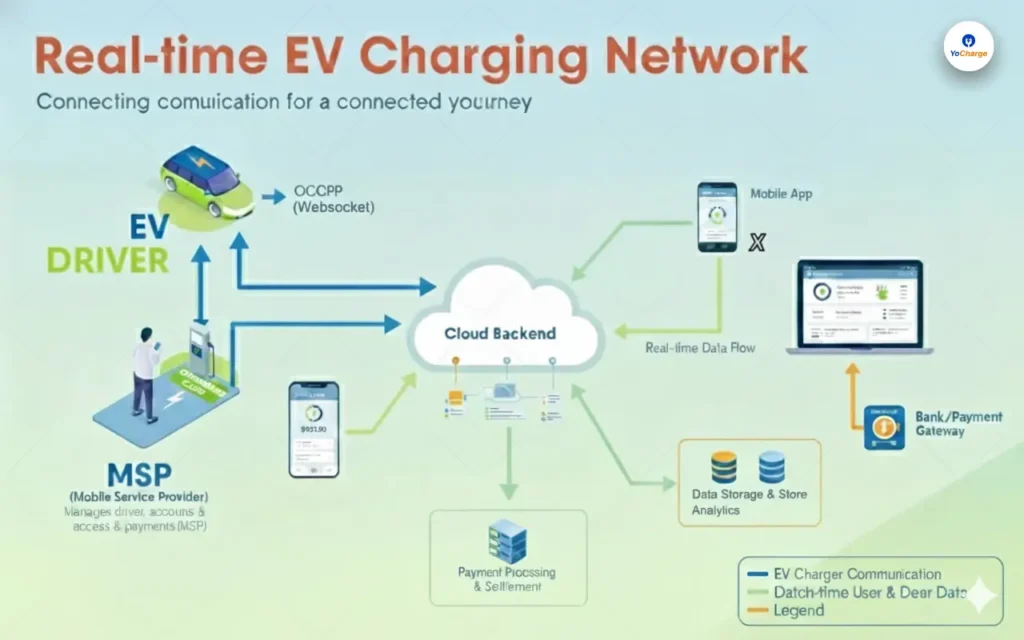
What is Fast EV Charging Technology?
Fast EV charging technology allows electric vehicles to recharge their batteries quickly. Unlike standard chargers, fast chargers deliver a higher power output, reducing charging time.
Fast chargers are categorized based on their power delivery. These categories include:
- Level 1 Chargers: Basic chargers using household outlets (120V). These are slow and not considered fast charging.
- Level 2 Chargers: Faster chargers using 240V power. They are ideal for home and workplace use but not the fastest option.
- DC Fast Chargers: These chargers offer rapid power delivery directly to the battery. They are the primary focus of fast EV charging technology.
How Does Fast EV Charging Technology Work?
Fast EV chargers use direct current (DC) to deliver electricity directly to the battery. Traditional chargers first convert alternating current (AC) from the grid into DC before sending it to the battery. This conversion process limits speed. DC fast chargers bypass this step, providing power more efficiently.
Key components of fast EV chargers include:
- Power Modules: These control electricity flow to ensure safety and efficiency.
- Cooling Systems: Fast charging generates heat, so cooling is essential.
- Connectors and Cables: Standardized connectors, such as CCS and CHAdeMO, ensure compatibility with different EVs.
Types of Fast EV Charging Technology Standards
Fast EV charging technology relies on globally recognized standards. These include:
Combined Charging System (CCS)
- CCS combines AC and DC charging in a single connector.
- It supports high power levels, making it suitable for fast charging.
- Most European and American EVs use CCS.
CHAdeMO
- This standard originated in Japan and focuses on DC fast charging.
- It delivers up to 400 kW of power for ultra-fast charging.
- Nissan and Mitsubishi primarily use CHAdeMO.
Tesla Supercharger
- Tesla developed its proprietary fast-charging network.
- Superchargers can deliver up to 250 kW, reducing charging time significantly.
- Tesla now offers CCS adapters to expand compatibility.
GB/T
- This standard is common in China.
- It supports fast DC charging for vehicles in the Chinese market.
Also Read: Understanding EV Battery Recycling
Power Levels of Fast EV Charging Technology
Fast chargers offer different power levels. These power levels determine the charging speed:
- 50 kW Chargers: Suitable for moderate fast charging. They can provide 150 km of range in 30 minutes.
- 150 kW Chargers: These chargers deliver faster charging speeds. They are ideal for highways and public stations.
- 350 kW Ultra-Fast Chargers: These are the fastest chargers available. They can charge compatible EVs in 15-20 minutes.
Benefits of Fast EV Charging Technology
Fast EV charging technology offers several benefits for EV owners and the environment:
- Reduced Charging Time: EVs can charge in minutes instead of hours.
- Improved Convenience: Drivers can quickly recharge during long trips.
- Increased EV Adoption: Fast charging makes EVs more appealing to consumers.
- Environmental Benefits: Faster charging promotes the use of zero-emission vehicles.
- Support for Public Infrastructure: Fast chargers at public stations reduce range anxiety.
Challenges in Fast EV Charging Technology
While fast EV charging is promising, it faces several challenges:
- High Installation Costs: Fast chargers require significant investment in infrastructure.
- Grid Strain: Delivering high power levels can strain local electricity grids.
- Battery Degradation: Frequent fast charging can reduce battery lifespan.
- Compatibility Issues: Not all EVs support the same fast-charging standards.
- Land Requirements: Installing fast charging stations requires space, especially in urban areas.
Innovations in Fast EV Charging Technology
Recent advancements aim to overcome these challenges. Some notable innovations include:
- Solid-State Batteries: These batteries can handle higher charging speeds with less degradation.
- Wireless Charging: Inductive charging eliminates cables and simplifies the process.
- Energy Storage Systems: Integrating batteries into charging stations reduces grid dependency.
- Dynamic Charging: Charging EVs while they are in motion using embedded road systems.
- High-Efficiency Power Electronics: These components improve energy conversion and reduce losses.
Fast EV Charging Technology Networks Around the World
Countries worldwide are investing in fast EV charging networks:
United States
- Tesla’s Supercharger network leads in coverage and reliability.
- Electrify America and ChargePoint offer extensive fast-charging options.
Europe
- Ionity, a joint venture of automakers, supports CCS chargers across Europe.
- Fastned provides ultra-fast chargers with renewable energy.
China
- China has the largest network of fast chargers using the GB/T standard.
- Companies like Contemporary Amperex Technology Limited are driving innovation in battery technology.
India
- India focuses on deploying fast chargers in urban and highway areas.
- Government incentives promote EV adoption and charging infrastructure.
Future of Fast EV Charging Technology
The future of fast EV charging technology looks promising. Here are key trends to watch:
- Ultra-Fast Charging: Chargers delivering over 500 kW will become common.
- Smart Charging Systems: Integration with IoT and AI will optimize charging schedules.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Solar and wind power will fuel charging stations.
- Standardization: Global standards will improve compatibility across EV brands.
- Affordability: Innovations will reduce costs for consumers and businesses.
Also Read: EV Charging Charges in Different Countries
Environmental Impact of Fast EV Charging Technology
Fast EV charging technology supports sustainability efforts. By enabling quick recharges, it encourages the use of EVs over traditional vehicles. However, there are challenges:
- Energy Sources: Charging stations must rely on renewable energy to reduce carbon emissions.
- Recycling Batteries: Proper disposal and recycling of EV batteries are essential.
- Efficient Grid Management: Energy storage solutions can balance demand and supply.
Conclusion
Fast EV charging technology is transforming the way we use electric vehicles. It addresses one of the biggest concerns of EV owners: charging time. With innovations and global efforts, fast charging will make EVs more practical and accessible.
Challenges like grid strain and battery degradation remain but are solvable with continued advancements.