EV Terminology
Glossary, Definitions & Terminology Related to EV & Charging
This page summarises glossary of important terms, relevant definitions and basic Terminology used in context of Electric Vehicles & EV Charging. Yocharge EV terminologies will give you a thorough understanding of the most common and typical EV charging terms that existed in the EV ecosystem. This article covers various topics from main stakeholders to technical terms regarding EV charging, such as chargers, protocols, management systems, battery systems etc.
Basic EV Charging Terminology:
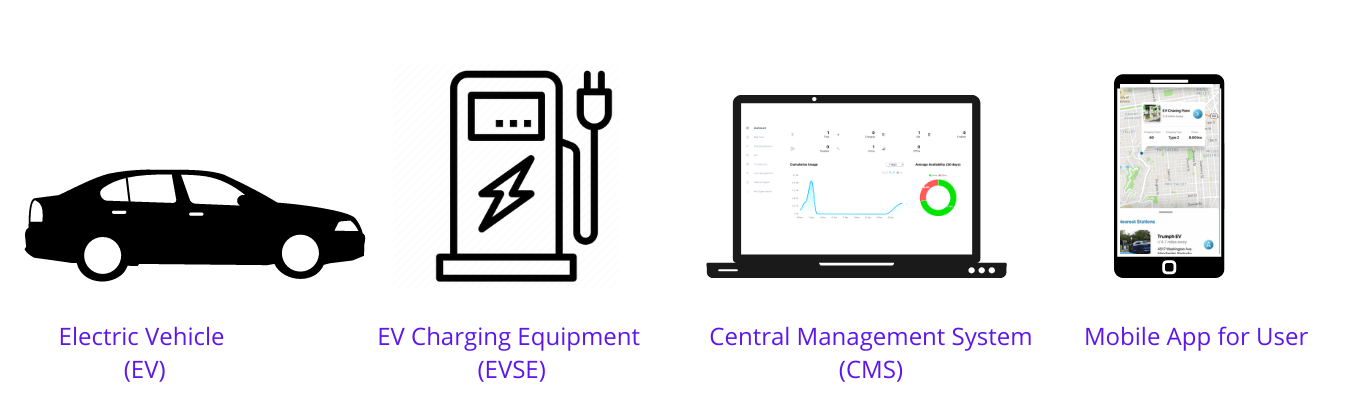
Electric Vehicle (EV): Electric Vehicles (EVs) are run by electric motors which are powered by energy stored in batteries. EVs have an electric motor instead of an Internal Combustion Engine (ICE). As an EV runs on electricity, the vehicle emits no exhaust from a tailpipe i.e. it has zero tail pipe emission and does not contain components, such as a fuel pump, fuel line, or fuel tank. | Read Ahead: Different types of EVs
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment(EVSE): An EVSE supplies electrical energy to charge EVs. The EVSE system includes electrical conductors, related equipment, software, and communications protocols that deliver energy efficiently to electric vehicle. As per Ministry of Power guidelines, Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE) shall mean an element in electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure that supplies electric energy for recharging the battery of electric vehicles.
Central Management System (CMS): An intelligent back-end solution that enables real-time data sharing between the electric vehicle, its charger and the charge-point operator. The Central Management System also called as Charging Management Software or Charging Station Management Software is the technology stack that allows Charge Point Operators (CPO’s) to operate & manage their charging stations.
Charge point operator (CPO): An entity that installs and manages the operations of the charging infrastructure. A CPO may own the charging infrastructure or provide services on behalf of the charge point owner.
Public Charging Station (PCS): An EV charging station where any electric vehicle can get its battery recharged.
Battery Charging Station (BCS): BCS are stations where the discharged or partially discharged electric batteries for electric vehicles are electrically recharged. For all practical purposes, Battery Charging Station (BCS) shall be treated at par with Public Charging Station (PCS), and the applicable tariff for electricity supply shall also be same as for PCS.
Captive Charging Station (CCS): An electric vehicle charging station exclusively for the electric vehicles owned or under the control of the owner of the charging station e.g. Government Departments, Corporate houses, Bus Depots, charging stations owned by the fleet owners etc. and shall not be used for commercial purpose.
Battery Swapping Station (BSS): BSS are stations where any electric vehicle can get its discharged battery or partially charged battery replaced by a charged battery.
- Note: Most EVs have an on-board charger that converts AC current to DC current as all batteries require DC power to charge. None of the existing and upcoming models in India have an on-board charger that has capacity to utilize a 22 KW AC charging.

Detailed EV related Terminology
A-Z Glossary for EV Users
YoCharge wants to engage everyone in the electric vehicle and EV charging business. From batteries to charging, the complete guide below serves as a quick reference for current and potential EV users.
A
- AC (alternating current): A form of electric current that reverses direction at regular intervals. Consumers typically use it when they plug-in Televisions, fans and kitchen appliances, etc.
- Amp (short for Ampere): Unit to measure electric current.
B
- Battery: The battery is the energy centre of the EV and can be recharged by plugging in the charging point.
- BEV (battery electric vehicle): The BEV utilises energy stored in rechargeable battery packs.
- Battery Management system: It is an electronic system installed inside vehicles to manage and protect the battery.
C
- Charging: EV requires an EV charger to keep the battery range full. Just like modern chargeable devices, EVs also have a charging battery charging process.
- Charging Point: It is a point or outlet which supplies electrical power for charging EVs.
- Charging station: refers to site or facility or infrastructure with one or more Charge Points.
- CHAdeMO: The full form of CHAdeMO is CHarge de MOve. It is a fast DC charging standard charger for EVs. It is a standard set by five major Japanese automakers; now, it is used globally.
- CCS (combined charging system): It charges EVs using standard AC and DC vehicle connectors and can be charged via vehicle inlet. It is a European standard connector used globally.
- CMS (charging management system): It is a system built to manage, optimise and control the EV charging process.
- CPO (charge point operator): Install, manage and ensure optimal operations of chargers.
D
- DC (direct current): It is one directional flow of electric current. Fast chargers of EVs use DC charging.
- DC fast charging: This type of charging is primarily available at public charging stations and offers an accelerated charging facility. The high power transfer charges EV faster.
E
- EV (electric vehicle): A vehicle which is solely powered by electricity.
- EVSE (electric vehicle supply equipment): It is an infrastructure designed to supply power to EVs.
- EREV (extended-range): The extended-range electric vehicle features an auxiliary power unit to electric cars. It is usually an internal combustion engine that acts as a generator to recharge the battery when it runs out.
F
- FCEV(fuel cell electric vehicle): It is a type of EV that uses a fuel cell instead of a battery and provides a combination option with a battery.
G
- Greenhouse gases: Conventional vehicles emit greenhouse gases (such as carbon dioxide and methane). These gases are the ultimate causes of global warming.
- Grid: It is an electricity supply mechanism. An EV draws power from the grid.
H
- HEV: The heavy electric vehicle utilises a dual system of electric propulsion and an internal combustion engine.
- Home charging: Now a user can plug in an EV in-home charger available in the parking area. These home chargers are typically the type of overnight charging dedicated for home charging as one of the safest way.
I
- ICE (Internal combustion engine): It is an engine powered by fuel in the form of petrol or diesel.
- Incentives: The government offer benefits to encourage more sales in the EV market.
K
- kW (Kilowatt): It is a unit for measuring real-time electrical power. It is the rate at which power is transferred from a charging station to an electric vehicle.
- kWh (Kilowatt-hour) It is the unit of measurement of electricity. A kilowatt-hour (kWh) measures how much energy is transferred from the charging station to your electric car in one hour.
L
- Lithium-ion battery: Also known as a Li-ion battery, it is a common rechargeable battery.
- Level1 charging: It is a charging facility provided in a common household outlet up to 120v. It is the slowest method of charging and can take up to 24 hours to charge your EV.
- Level 2 charging: Charge your EV at 240v using public/private charging stations and a charger installed at the outlet. Level 2 chargers are the most recommended chargers to EV users.
- Level 3 charging: Also known as DC fast charging, it is the fastest way to charge an EV fully. It already takes half n hour to 45 minutes to charge an EV completely.
O
- OEM (Original equipment manufacturer): It is a manufacturer of vehicles, vehicle parts and related services. Thus the term is used as EV manufacturers.
- Off-peak charging: It is a method of charging an electric vehicle at a low cost during off-peak hours (usually at night).
- OCPP (open charge point protocol): It is a protocol of communication between EV charging stations & charging management systems. For a detailed analysis of OCPP, visit this link.
P
- PHEV (Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle): It is a hybrid electric vehicle whose battery pack can be recharged by plug-in or through an external power source.
- Public Charging: Charging infrastructure accessible to everyone.
R
- Range: It is the number of miles an electric vehicle can cover the total distance in one full charge before the battery signals for recharge.
- Range anxiety: It is the stress EV owners face when running out of battery power before the next charging station destination arrives.
- Regenerative braking: It is a method of braking used by an EV which generates energy from the braking of the vehicle stored and used.
- Renewable energy: It is a natural energy source that can be naturally replenished through solar, wind and water.
- Roaming: It helps drivers to charge their EV at charging stations of different networks using a single account.
S
- Smart charging: An internet connected charge point gives users a smart charging option and can perform energy monitoring, load balancing, and charging management. Read more at: Smart EV Charging
- SOC (State if charge): The charge level is relative to the battery’s capacity, which operates electrically.
T
- Tesla Supercharger: Tesla uses a modified version of the Type 2 Mennekes Plug. This supercharger allows Model S to recharge the battery to 80% within 30 minutes.
- TORQUE (The twisting force): It is a form of measure to determine the amount of a vehicle’s load at a given time. The load an engine can handle generates the amount of power to rotate on its axis. Petrol and diesel engines deliver torque over a curve as RPM increases. That is the peak power at a given RPM. Electric motors deliver maximum torque from zero revs, which means acceleration from a standstill is possibly phenomenal.
U
- Time of Day or Time of Use (TOU) tariff: The tariff rate charged to an EV user is based on the total electricity consumed and also upon the time of day the energy used. It may also be reffered to as Time of Day (ToD) tariff.
V
- V2G (vehicle to grid): It is a system that allows electric vehicles to communicate with the power grid and manage electricity flow in a set direction. It introduces a new scope of EV charging energy management. However, it is not very popular, and a small number of EV manufacturers use it. Read more at V2G. Read more on – V2G Charging
W
- Watt: It is a unit of electric power measure.
Z
- Zero-emission: Zero-emission vehicles emit no tailpipe pollutants from the onboard source of energy. Harmful particulates like hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, ozone, lead, and various oxides of nitrogen are emitted by conventional fuel vehicles. The electric vehicle emits zero pollutants and makes the environment pollution free. EVs emit no greenhouse gases.
We hope our EV terminology will help you in your research and current business setup. If you want to learn more about EV charging business opportunities, check our electric vehicle charging solutions for more details or