The availability of EV Charging stations were always a concern for EV users and the ones who are planning to shift into electric mobility. Government of India and other leading manufacturers in India are planning to set up EV Charging station across the country to increase the adoption of EVs by the end of 2030. So let us discuss about the types of EV charging station:
A. Types of EV Charging Station based on Power Output Rating

EV charging stations can be sub-classified into three:
- Level 1 EV charging stations
- Level 2 EV charging stations
- Level 3 EV charging stations
Let us discuss about each in detail :
A1. Level 1 Electric Vehicle Charging Station
Electric vehicle at Level 1 Chargers plug into a typical wall socket using a 120V AC plug delivering a 1.3 kW to 2.4 kW power output on average. This power output corresponds to an EV range of 5-8 kilometers per hour. There is no installation or additional hardware needed for these chargers. Home use of Level 1 electric vehicle chargers is common.
The least expensive charging stations are Level 1 electric chargers, however they also take the longest to fully charge your car’s battery. These types of chargers are frequently used by car owners to charge their cars overnight.
Common Level 1 electric vehicle charger manufacturers are delta, abb, teltonika, wallbox.
A2. Level 2 Electric Vehicle Charging Station
Level 2 Electric Vehicle Chargers are used in both household and commercial areas to charge EVs. While commercial chargers use 208 V AC plug the household charger used 240 V AC plug. Electric vehicle at Level 2 Chargers must go through a suitable installation procedure, which must be carried out by a qualified electrician.
Additionally, these chargers can be mounted as a component of a solar panel system. These chargers have an hourly charging capacity of 16 to 32 kilometers of range. A car battery can be fully charged in under two hours using a Level 2 electric vehicle charger. They are ideal for homes that need quick charging stations and businesses that want to provide clients fast charging options.
Common Level 2 electric vehicle charger manufacturers are ABB, Teltonika and Delta. While Nissan manufactures its own Level 2 EV chargers.
A3. Level 3 Electric Vehicle Charging Station
Level 3 electric car chargers also referred to as DC fast chargers provide your electric vehicle with a range of up to 160 kilometers or more. With just 30 to 40 minutes of charging, it can fully charge your vehicle. DC rapid chargers, however, are often only employed in industrial and commercial settings.
Installation and maintenance of these DC charging stations demand powerful, highly specialized equipment. These Level 3 Chargers are not compatible with all electric vehicles. While many Plug-in hybrid vehicles are not compatible with DC fast chargers. Higher voltage and direct current flow into the battery reduce the need for EV onboard charger installation in DC fast charging stations.
Hyundai Ioniq EV, Nissan leaf and Audi e-tron are some of the electric vehicles that supports DC fast charging standards.
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |
| Voltage | 120 V 1-Phase AC | 208 V or 240 V 1-Phase AC | 208 V or 480 V 3-Phase AC |
| Current rating | 12 – 16 Amps | 12 – 80 Amps (Usually 32 Amps) | Less than 125 Amps (Usually 60 Amps) |
| Charging Outlets | 1.4 to 1.9 kW | 2.5 to 19.2 kW (Usually 7 kW) | Less than 90 kW (Usually 50 kW) |
| Charging Time | 5-8 kilometers range per hour | 16 to 32 kilometers range per hour | 80% charged within 20 to 30 minutes |
| Applications | Used in residential applications | Used in both residential and commercial applications | Used in industrial, commercial, and fleet applications |
B. Types of EV Charging Station based on type of Current Output
B1. AC Charging station
- The AC EV Chargers take input AC current & provide AC output current. The ac current output from these chargers goes into the input of onboard charge controller (OBC) of electric vehicle which converts this ac current to dc current and feeds it to the battery. The ac chargers offer utility in terms of smart operation & metering, data analytics, safety, earthing & other checks etc.
B2. DC Charging station
The DC EV chargers take input of single or three phase AC current & provide output DC current. The output from these DC chargers bypasses the onboard charge controller and is directly fed into the battery.
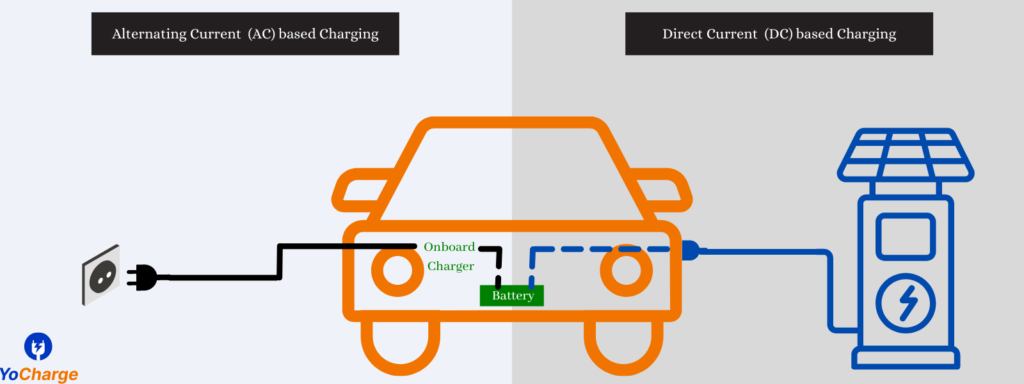
| Parameter | AC Charger | DC Charge |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Current | Provides AC Current to On-board Charger | Provides DC current directly to batteries |
| Cost | Relatively Cheaper | Higher Costs |
| Charging Speed | Usually limited by capacity of onboard chargers. | High Charging Speed, depends on DC Charger Capacity & Battery Voltage |
| Applications | Usually used at Home or destination chargers (overnight) | Usually used at midways, conventional fuel pumps & other fast charging locations. |
Read in Detail
C. Types of EV Charging Station based on Location
C1. Destination charging station
Destination charging stations are installed on places like residential buildings, malls, hotels, offices etc. These are normally low voltage (240/415 Volts) AC Chargers.
C2. On the Go charging station
On the go charging stations are installed on places like fuel pumps, highways, restaurants where EV users come, stop for a while, charge their vehicles and go. These are usually high voltage and usually they consist of DC Fast Chargers that can charge in short duration. These charging stations are usually integrated with an EV Charging Management System that allows EV users to operate these charging stations by themselves through a mobile app or smart cards.
Check Out
Launch your own EV Charging brand in 7 days without any technology development & manpower deployment. Completely automated solution with admin dashboards & branded mobile applications.