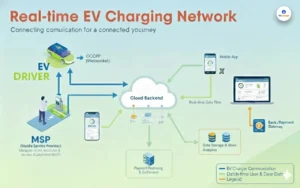
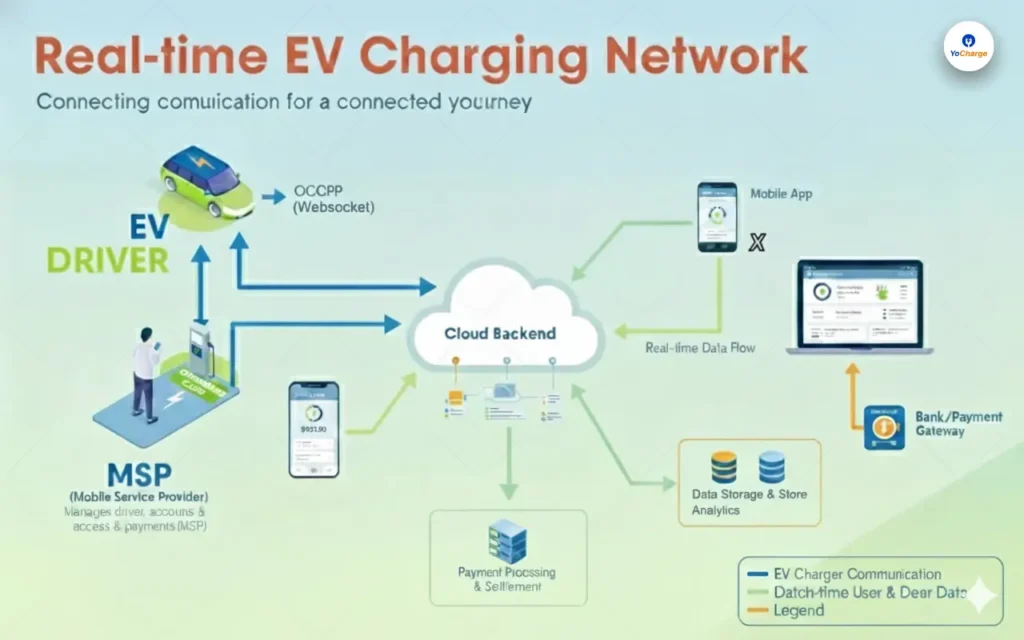
As the global shift toward sustainable transportation accelerates, two major options are rising in popularity: Flex Fuel Cars and Electric Cars. Both technologies aim to reduce the environmental impact of traditional gasoline vehicles, but they do so in different ways.
This article provides a detailed comparison of Flex Fuel Cars and Electric Cars, exploring their pros, cons, and the role each plays in a greener future.
What Are Flex Fuel Cars?
Flex Fuel Cars (Flexible Fuel Vehicles) can run on more than one fuel type. These cars use a mixture of ethanol and gasoline, usually in a 51% to 85% ethanol (E85) and a blend of gasoline.
Ethanol is derived from renewable resources like corn and sugarcane, making it more environmentally friendly than fossil fuels. In the U.S., over 20.9 million Flex Fuel Vehicles were on the roads as of 2022, according to the U.S Department of Energy.
What Are Electric Cars?
Electric Cars, or Electric Vehicles (EVs), are powered entirely by electricity. They do not require gasoline or any other traditional fuel. Instead, they rely on rechargeable batteries to store energy. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, making them highly eco-friendly.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), EV sales reached 10 million in 2022, representing a 14% share of global car sales.
Flex Fuel Cars vs Electric Cars
The rise of alternative energy vehicles has sparked a growing debate: which is better, Flex Fuel Cars or Electric Cars? Both options offer greener alternatives to traditional gasoline vehicles, but they approach sustainability differently.
Let’s explore their differences in terms of environmental impact, infrastructure, costs, and more.
Environmental Impact
One of the most crucial aspects of any vehicle in today’s world is its environmental footprint. Flex Fuel and Electric Cars both aim to reduce emissions, but they do so in distinct ways. Let’s examine the environmental implications of each.
Flex Fuel Cars
Flex Fuel Cars offers reduced carbon emissions when using ethanol. Ethanol produces less carbon dioxide (CO2) than gasoline, helping to reduce greenhouse gases. However, Flex Fuel Cars are not entirely carbon-neutral.
Ethanol production requires large-scale farming, which can lead to deforestation, water usage, and other environmental issues. Moreover, when these cars run on gasoline (if E85 isn’t available), they emit as much CO2 as conventional cars.
According to eFlexFuel, the use of E85 ethanol can reduce lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions by up to 34%. However, the actual reduction depends on the type of ethanol and how it is produced.
Electric Cars
Electric Cars are considered a much cleaner option because they produce no tailpipe emissions. However, their environmental impact depends on the source of electricity used for charging.
If the electricity comes from renewable sources like wind or solar power, the environmental benefits are significant. On the other hand, if the power comes from coal or natural gas, the net benefit diminishes.
Fueling and Charging Infrastructure
Access to fuel or charging stations is key to a vehicle’s convenience and usability. While Flex Fuel Cars rely on gasoline or ethanol, Electric Cars depend on charging networks. Here is how each type of vehicle fares in terms of infrastructure availability and growth.
Flex Fuel Cars
One of the major advantages of Flex Fuel Cars is their ability to run on gasoline when ethanol isn’t available. This makes them highly versatile. However, E85 fueling stations are not as common as gasoline stations.
In the U.S., there are around 4,300 E85 fueling stations, compared to over 196,643 gasoline stations. The lack of widespread availability can limit the use of ethanol as the primary fuel.
Electric Cars
Electric charging infrastructure is rapidly expanding. According to the Federal Highway Administration, there are around 196,000 publically available charging ports in the U.S. alone.
Globally, governments are pushing for even more growth in charging infrastructure, with countries like the U.S., China, and those in Europe leading the way.
However, long charging times and limited availability in rural areas still present challenges for EV drivers.
Cost Efficiency
For many consumers, cost efficiency is a major factor when choosing a vehicle. The costs of buying, operating, and maintaining Flex Fuel Cars and Electric Cars differ significantly. Let’s compare how much each option impacts your wallet over time.
Flex Fuel Cars
The cost of fueling a Flex Fuel Car depends on local gasoline and ethanol prices. Ethanol (E85) is often cheaper per gallon than gasoline. However, Flex Fuel Cars typically get fewer miles per gallon on ethanol than on gasoline.
For example, a car that gets 25 miles per gallon (MPG) on gasoline might only get 18 MPG on E85. This lower fuel efficiency offsets some of the cost savings.
Electric Cars
Electric Cars are far more cost-efficient to operate than gasoline or Flex Fuel Cars. The average cost to drive an electric car is about $0.05 per mile, compared to $0.12 per mile for gasoline vehicles.
However, EVs typically have a higher upfront cost. The average price of an EV in the U.S. is around $54,000, while conventional cars average $34,000.
That said, the total cost of ownership often tips in favor of EVs due to lower fuel costs, fewer maintenance requirements, and government incentives. EVs have fewer moving parts, meaning lower maintenance costs and longer intervals between services.
Performance and Driving Experience
While sustainability is important, so is the driving experience. Performance is an area where these two types of vehicles differ. From acceleration to handling, here’s what you can expect when driving a Flex Fuel Car versus an Electric Car.
Flex Fuel Cars
Flex Fuel Cars perform similarly to traditional gasoline cars. They have a familiar driving experience, and the switch between ethanol and gasoline is seamless.
However, they might exhibit reduced fuel efficiency when using ethanol due to its lower energy content compared to gasoline.
Electric Cars
Electric Cars offer a very different driving experience. They provide instant torque, meaning faster acceleration and smoother handling. Many EV owners report a quieter and more enjoyable ride compared to gasoline vehicles.
However, driving range anxiety—the fear that the battery will run out before reaching a charging station—remains a concern for some drivers. The average range for EVs is around 110 to 300 miles with newer electric vehicle models.
Availability and Adoption
The adoption rate of Flex Fuel Cars and Electric Cars reflects market trends and consumer preferences. Both technologies are making inroads, but they do so at different paces. Let’s explore how readily available each option is and what the adoption trends suggest.
Flex Fuel Cars
Flex Fuel Cars are widely available, especially in the U.S., Brazil, and parts of Europe. Automakers like Ford, GM, and Chrysler have been producing Flex Fuel models for over two decades. Despite their availability, consumer adoption is relatively low.
Electric Cars
Electric Cars have experienced a surge in popularity in recent years. Global EV sales increased by 35% in 2023, with countries like USA, Norway, Germany, and China leading the adoption.
Automakers like Tesla, Nissan, and BMW are continually expanding their EV offerings, while governments are providing incentives and subsidies to promote EV adoption.
Future Outlook of Flex Fuel Cars vs Electric Vehicles
The future of Flex Fuel Cars largely depends on the availability and production of ethanol. As governments aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, ethanol will likely remain a viable option.
However, with the rise of electric vehicles and advancements in battery technology, the role of Flex Fuel Cars may diminish over time.
The future for Electric Cars looks brighter. With falling battery costs, expanding infrastructure, and increasing governmental support, EVs are expected to dominate the automotive industry.
According to Bloomberg New Energy Finance, EVs could account for 58% of global passenger vehicle sales by 2040.
Which Is Better: Flex Fuel Cars or Electric Cars?
Both Flex Fuel Cars and Electric Cars have their advantages, but Electric Cars offer more long-term benefits in terms of cost efficiency, environmental impact, and future scalability. Flex Fuel Cars provide flexibility and can be an option for those in areas without reliable EV charging infrastructure.
However, as electric infrastructure continues to grow, Electric Cars are expected to become the preferred choice for eco-conscious consumers.
If you are considering making a greener choice for your next vehicle, the long-term potential and sustainability of Electric Cars make them a strong contender for future transportation.
If you are ready to lead the way in the transition to electric vehicles, YoCharge’s Best EV Charging Management Software offers everything you need to build and manage an EV charging network and electric vehicles effectively.
Contact YoCharge today to learn more about how our premium Charging Management System can empower your EV charging network.
Read Latest Articles or News