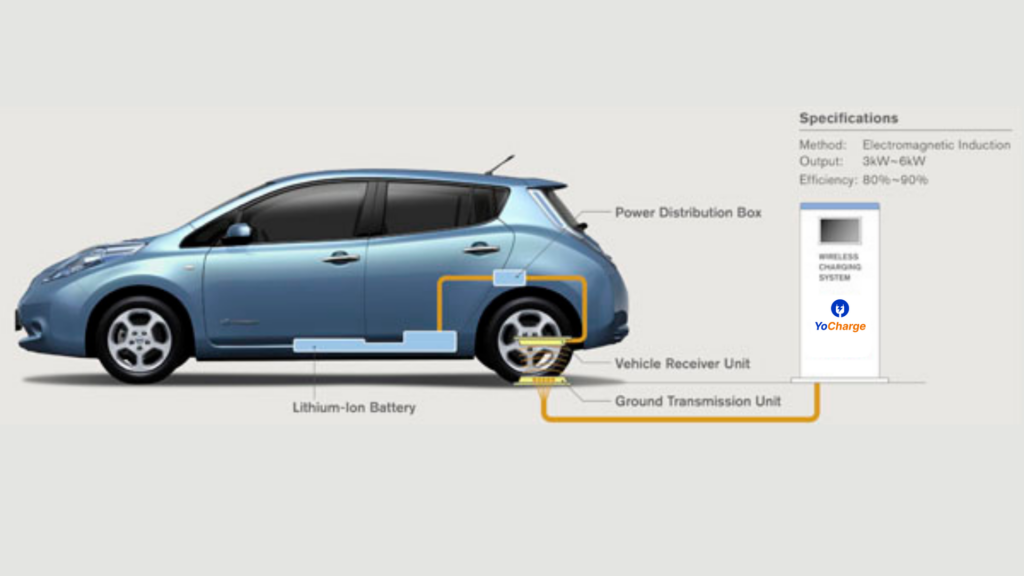
Induction wireless charging is a form of wireless power transfer that is frequently referred to as wireless charging or cordless charging. Electricity is delivered to portable devices using electromagnetic induction. Electric toothbrushes, power tools, vehicles, and medical equipment use inductive charging. Without needing to be properly aligned or make electrical contact with a socket, portable equipment can be put close to a charging station or inductive pad i.e. wireless connection.
Working Principle
Induction wireless charging is named as such because it transfers energy through inductive coupling. An induction coil in the charging station or pad is first subjected to alternating current. The magnetic field is produced by the flowing electric charge and is subject to variations in strength due to variations in the amplitude of the electric current. In the induction coil of the portable device, this shifting magnetic field generates an alternating electric current, which is then passed through a rectifier which converts it into direct current. Finally, the direct current supplies electricity or charges a battery.
Applications
The applications of induction wireless charging can be categorized into two. One is high power and the other is low power applications.
- Low power applications: Small consumer electronics devices, such mobile phones, handheld gadgets, some PCs, and similar devices, which typically charge at power levels below 100 watts, are typically supported by low power applications. Usually, the 50 or 60 Hertz AC utility frequency is used for low power applications.
- High power applications: Inductive battery charging at power levels more than 1 kilowatt is referred to as high power inductive charging. High-power inductive charging has several uses, but it is most commonly used to power electric vehicles. Inductive charging offers a cordless, automated alternative to plug-in charging. These devices can have power outputs of up to 300 kilowatts, or about 1 kilowatt. All high-power inductive charging systems require primary and secondary coils that are tuned to resonance. With frequencies reaching up to 130 kHz, these devices operate in the long wave spectrum. Short wave frequencies can increase the system’s effectiveness and scale, but they would eventually transmit the signal over the planet. High power applications have concerns regarding radio frequency interference and electromagnetic compatibility.
Advantages
- Protected connections – When the electronics are contained and kept away from water and oxygen in the air, there will be no corrosion. Less chance of insulation failure leading to electrical failures like short circuits, especially in areas where connections are made or broken repeatedly.
- Durability – The gadget’s socket and connecting cable experience substantially less wear and tear when the item isn’t constantly plugged in and out.
- Greater visual appeal and convenience – Since the induction charging is wireless no cables are required.
- Convenient electric vehicle charging – Automated high power inductive charging of electric cars facilitates more frequent charging sessions and extends the driving range.
- Less reliability on manual support – Without the need for individuals to plug and unplug, inductive charging systems can run independently. Consequently, reliability is increased.
- Not weather dependent – The advantage of an inductive charger is that it offers electrical safety in all kinds of weather.
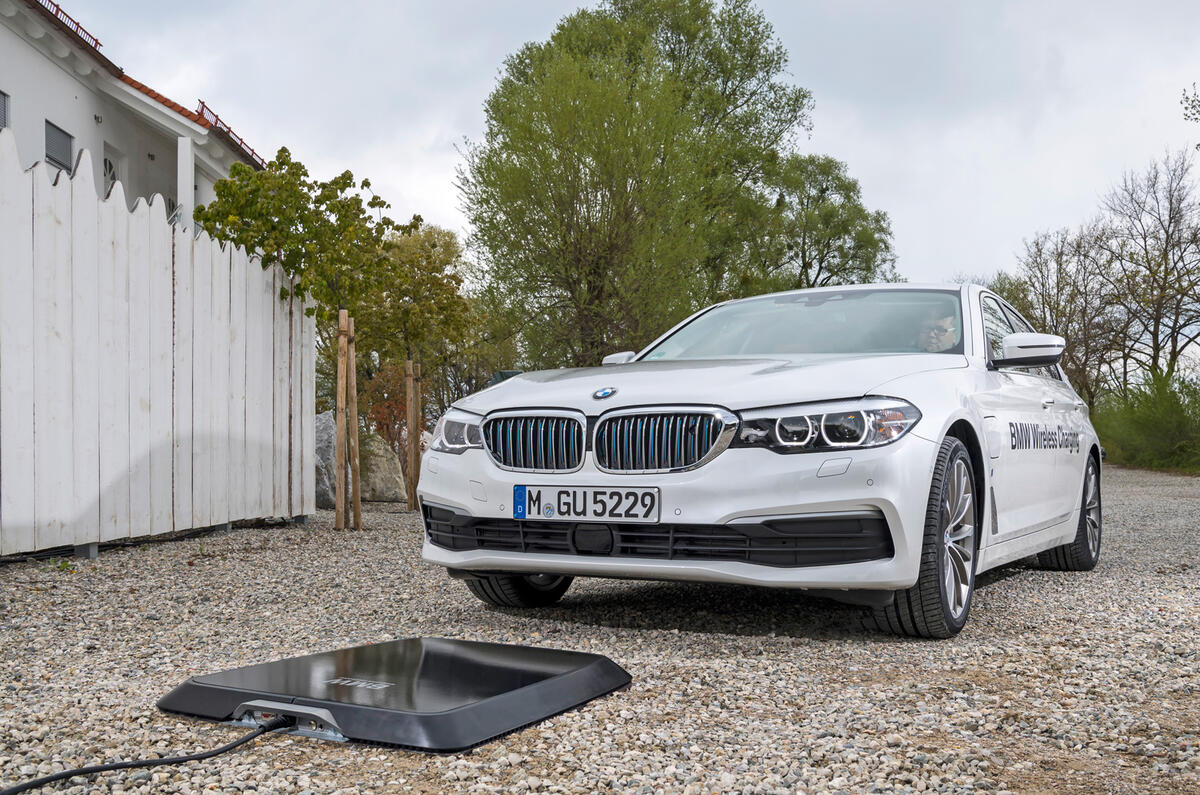

Disadvantages
- Slower charging – Even with the same amount of power supplied, gadgets require 15% more time to charge than conventional charging as a result of the reduced efficiency.
- More expensive — Inductive charging additionally requires drive electronics and coils in the device and charger, which increases manufacturing complexity and costs.
- Standards compatibility – Not all gadgets are able to use various inductive chargers. Some gadgets, however, started to support a number of standards.
- Offers less flexibility – In terms of flexibility, the method is really no different from utilizing a charging station with a connection because it only functions over short distances and requires alignment between the power transmitter and power receiver.