Open Automated Demand Response (OpenADR) is a research and standards development effort for energy management led by North American research labs and companies. The typical use is to send information and signals to cause electrical power-using devices to be turned off during periods of high demand.
Understanding Open ADR
Open Automated Demand Response (Open ADR) offers a common language energy customers and grid operators can use to communicate.
Born out of research from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Open ADR is designed to facilitate the automatic exchange of information between utilities, energy management control systems, and customer-owned energy resources, including Electric Vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure.
Evolution of Open ADR
- In 2002, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory started researching on ADR in response to the California electricity crisis of 2000 & 2001(ref).
- In May 2010, OpenADR became one of the first 16 Smart Grid Standards supported by the U.S. Department of Energy the National Institute of Standards and Technology Smart Grid Interoperability Standards effort.
- In January 2019, it was approved as a global standard by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), which publishes consensus-based standards for the world’s electric systems.
OpenADR Alliance

The OpenADR Alliance has been created to standardize, automate, and simplify Demand Response (DR) and Distributed Energy Resources (DER) to enable utilities and aggregators to cost-effectively manage growing energy demand & decentralized energy production, and customers to control their energy future.
The OpenADR Alliance is a California-based nonprofit 501(c)(6) corporation. It is composed of industry stakeholders that are interested in fostering and accelerating the development and adoption of OpenADR standards and compliance with those standards.
Open ADR Frameworks:
Open Automated Demand Response (OpenADR) frameworks provide a non-proprietary, open standardized DR interface that allows electricity providers to communicate DR signals directly to existing customers using a common language and existing communications such as the Internet.
OpenADR 1.0
The initial OpenADR 1.0 framework was refined in partnership with a standards development organization, OASIS (Open Standards, Open Source), to make it fully compliant with the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Smart Grid Interoperability Framework.
OpenADR 2.0
OpenADR 2.0, the basis of today’s global standard, is managed by the OpenADR Alliance. This framework is now in use in several states of USA, parts of Europe, China, Japan, Australia and Korea.
OpenADR 2.0 Profiles
The OpenADR Alliance has defined several profiles to accommodate a variety of different devices for varying applications.
- The OpenADR 2.0a Profile is intended for simple devices (thermostats, electric water heaters, etc.) with limited computing and memory capacity. The profile is designed for resource-constrained, low-end embedded devices that can support basic DR services and markets.
- The OpenADR 2.0b Profile is intended for high-end embedded devices that can support most DR services and markets. Profile B contains an extensive list of commands and includes a flexible reporting (feedback) mechanism for past, current and future data reports.
- The OpenADR 2.0c Profile – is intended for wholesale market communication between ISO/RTO, aggregators, and utilities but it not completed yet.
Nodes in OpenADR
Message exchange in OpenADR takes place between two primary layers – VTN & VEN.
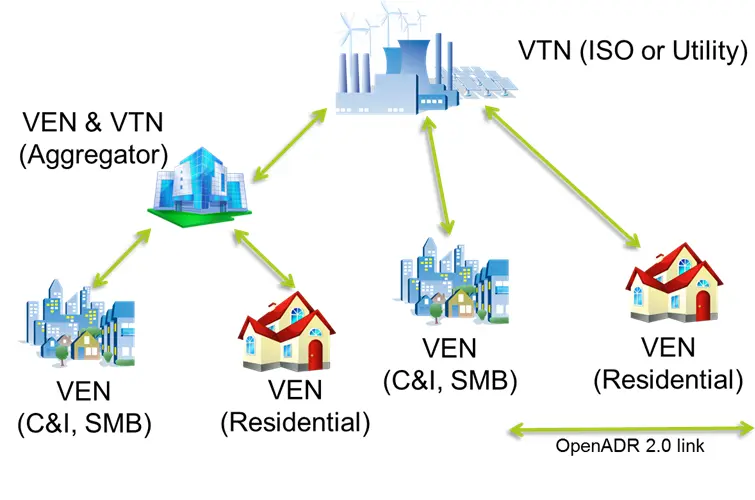
VTN
- VTN stands for – Virtual Top Node.
- A VTN is typically a “server” that transmits OpenADR signals to end devices or other intermediate servers.
VEN
- VEN stands for – Virtual End Node.
- A VEN is typically a “client” and can be an “Energy Management System” (EMS), a thermostat or other end device that accepts the OpenADR signal from a server (VTN).