Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Imagine a vehicle that glides through the bustling city streets, barely making a sound, consuming far less fuel, and emitting a fraction of the pollutants of traditional cars. This is not science fiction but the reality of Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs).
As climate change concerns rise and cities become more congested, the need for cleaner, smarter transportation solutions becomes imperative.
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) offer a bridge between conventional gasoline-powered cars and the fully electric vehicles of the future, blending the best of both worlds.
Let’s dive deeper into the fascinating technology of HEVs, their benefits, how they work, and what the future holds.
What Are Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)?
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) are cars that combine an internal combustion engine (ICE) with an electric motor, offering a balance of fuel efficiency and power.
Unlike conventional vehicles that rely solely on gasoline or diesel, HEVs alternate between or simultaneously use the ICE and electric motor, depending on driving conditions.
This intelligent synergy not only conserves fuel but also reduces emissions.
HEVs are designed to maximize efficiency in various driving scenarios, such as city driving, where frequent stops and starts to waste significant fuel.
By utilizing electric power at low speeds or when idle, HEVs can minimize fuel consumption, making them ideal for urban environments.
How Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) Work?
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) employ a unique powertrain configuration that allows them to switch seamlessly between the ICE and electric motor. Here’s a breakdown of how they operate:
- Battery and Electric Motor: The battery in an HEV powers the electric motor, which assists the engine, particularly at lower speeds. This motor generates additional torque and can propel the car without using the ICE in specific scenarios, such as city driving or when idling.
- Internal Combustion Engine (ICE): HEVs use gasoline or diesel engines to power the vehicle at higher speeds or when rapid acceleration is needed. The ICE also helps recharge the battery while driving, ensuring continuous operation.
- Regenerative Braking: When the driver applies the brakes, HEVs convert kinetic energy from the wheels into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery. This process, known as regenerative braking, improves overall efficiency and extends battery life.
- Power Control Unit (PCU): The PCU in HEVs manages the balance between the ICE and electric motor, ensuring that the vehicle runs as efficiently as possible. It decides when to engage the electric motor, ICE, or both, based on the speed, acceleration, and battery level.
This intricate system allows Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) to optimize power consumption, reduce fuel use, and emit fewer pollutants compared to traditional vehicles.
Types of Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)

Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) come in several forms, each tailored to different driving needs and levels of efficiency:
- Mild Hybrid (MHEVs): MHEVs use a small electric motor to support the engine but cannot operate independently. They provide a slight boost in fuel economy and emissions reduction, suitable for those seeking mild energy savings without switching entirely to electric propulsion.
- Full Hybrid (FHEVs): These HEVs can switch between the ICE and electric motor or use both simultaneously. Full hybrids can drive short distances on electric power alone, making them ideal for city driving and fuel savings in stop-and-go traffic.
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs): PHEVs come with a larger battery that can be recharged through an external power source. They offer extended electric-only ranges, typically between 20 to 50 miles, before the ICE engages. PHEVs are an excellent choice for those looking to drive mainly on electric power but need the security of a gasoline backup for longer trips.
Benefits of Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)
The advantages of Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) extend beyond just fuel savings. They address some of the most pressing issues of modern transportation, including emissions, urban pollution, and reliance on fossil fuels.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: By combining an ICE with an electric motor, HEVs achieve greater fuel economy, especially in city driving. This reduces fuel expenses and offers a more economical solution for those who drive frequently.
- Reduced Emissions: HEVs emit significantly fewer greenhouse gases than conventional vehicles, contributing to cleaner air and a lower carbon footprint. This advantage is particularly beneficial in congested cities where pollution is a significant concern.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: HEVs experience less wear and tear on the engine since it does not run continuously. Regenerative braking also reduces brake wear, meaning less frequent maintenance and replacement costs.
- Extended Range: Unlike fully electric vehicles (EVs), which may have range limitations, Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) offer the advantage of longer travel ranges by switching to the ICE when the battery is depleted.
- Energy Security: By decreasing dependence on fossil fuels, HEVs contribute to energy security and lessen vulnerability to fluctuations in oil prices.
Challenges Facing Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)
While Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) present numerous benefits, they are not without challenges:
- Higher Initial Cost: HEVs often have a higher upfront cost compared to traditional vehicles due to the complexity of their dual power systems and advanced batteries.
- Battery Lifespan and Replacement: Although HEV batteries are designed to last, they eventually need replacement, which can be costly. Technological advancements are making batteries more durable, but this remains a consideration for potential buyers.
- Environmental Concerns of Battery Production: The production of HEV batteries involves mining and processing metals like lithium and cobalt, which have environmental impacts. Recycling programs and advancements in battery technology are helping to mitigate these issues.
- Limited Electric Range (for Non-Plug-In Models): Unlike fully electric or PHEV models, standard HEVs have a limited electric-only range. This limitation makes them less ideal for those looking for extensive all-electric driving capabilities.
The Future of Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)
The trajectory of Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) is promising, with continuous advancements in battery technology, power management, and regenerative braking. Here are some trends shaping the future of HEVs:
- Improved Battery Technology: Innovations in lithium-ion batteries and the exploration of solid-state batteries promise extended range, faster charging, and enhanced durability.
- Increased Adoption of Plug-In Models: As charging infrastructure expands, PHEVs are expected to grow in popularity, offering the best of both electric and gasoline-powered driving.
- Enhanced Integration with Renewable Energy: Some manufacturers are exploring ways to integrate HEVs with solar panels, allowing vehicles to charge partially through solar power, making them even more sustainable.
- Autonomous Hybrid Vehicles: The future of HEVs might also include autonomous driving technologies, creating a new dimension in energy-efficient, self-driving vehicles for public transportation and personal use.
Popular Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)
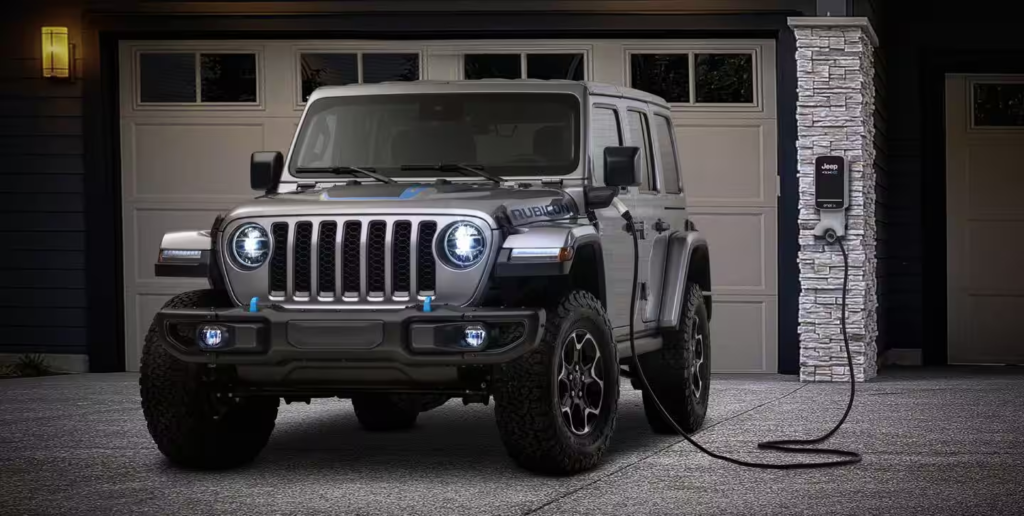

Here are some popular Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) in 2024:
- Toyota Prius Prime: Toyota Prius Prime is known for its exceptional efficiency, offering an electric range of 45 miles and a combined fuel economy of 52 mpg.
- Toyota RAV4 Prime: The Toyota RAV4 Prime features a plug-in hybrid system that provides an electric range of 42 miles and a combined fuel efficiency of 38 mpg.
- Chrysler Pacifica PHEV: The Chrysler Pacifica PHEV is designed for larger families, providing an electric range of 32 miles and a combined fuel economy of 30 mpg.
- Jeep Wrangler 4xe: The Jeep Wrangler 4xe combines off-road capability with hybrid efficiency, offering an electric range of 22 miles and a combined fuel economy of 20 mpg.
Final Thoughts on Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) represent a pivotal step towards more sustainable, efficient transportation. By merging the reliability of traditional engines with the benefits of electric power, HEVs offer a practical and eco-friendly solution for today’s drivers.
As the automotive industry evolves and new technologies emerge, HEVs are expected to play an integral role in the transition to a cleaner, greener future.
Whether you are looking for fuel savings, reduced emissions, or the flexibility of dual power, HEVs stand as a smart choice in the journey towards more responsible transportation.