As electric vehicles (EVs) proliferate, the need for a seamless charging experience becomes paramount. EV roaming protocols play a pivotal role in enabling seamless charging across various networks with only a single user registration based on roaming agreement between operators. Such EV roaming service provider, referred to as eMSP, enter into agreements with charge point operators (CPOs) and implement a ev roaming communication system based on open protocols. In this article, we shall discuss in some details what are these protocols and their unique advantages & differences.
What is EV Roaming ?
EV roaming simplifies the charging process by allowing EVs to charge on different charging networks without the need to create multiple subscriptions. To get the better idea, we can refer to roaming in context of mobile phone network.
Essentially, mobile phone network roaming allows you to continue enjoy the call connectivity even when there is no physical network of your service provider. The switch to partner network is made automatically and there is no need for you to subscribe to secondary network. Similarly, in ev roaming you can charge across multiple networks while using the account of your service provide without the need to create new accounts.
Thus EV Roaming allows you to have seamless charging experience without having to worry about actual Charging Station Operator or maintaining wallet balances in multiple accounts.
Key players in the ev roaming
Ev roaming consists of three key players:
- Charge point operators (CPOs) that own and/or operate a charging network
- eMobility service providers (EMSPs) offering network access via an app or charge key
- Roaming platforms, which enable roaming agreements between the CPOs and EMSPs
Models for EV Roaming
There are essentially two modes through which communication happens during ev roaming:
- Roaming via peer-to-peer data exchange eMSPs and CPOs through an ev roaming protocol. This includes bilateral agreements between two service providers.
- Roaming via hub: where data exchange between eMSPs and CPOs via one or multiple hubs that are a module. These hubs create one centralised roaming network open to all its members. Then enable their members to access various e-mobility partners.
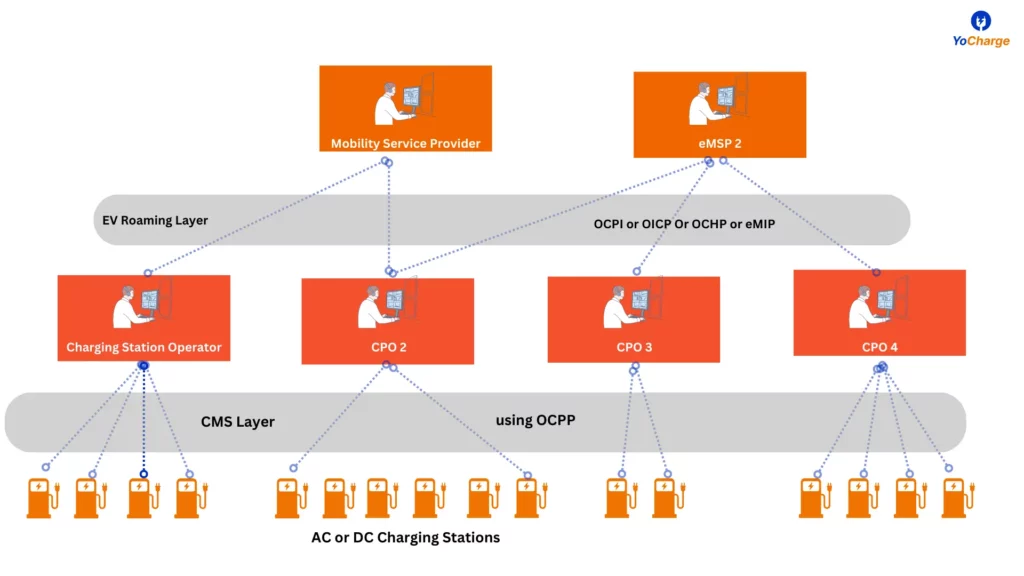
EV Roaming Protocols
The EV Roaming Protocols facilitate the communication between your native charging service provider, referred to as eMSP and the different charging station operators. eMSP’s and CPO’s use these protocols to exchange information on charge point, tariff as well as offer advanced features like reservation, payments, app-based remote start and stop of charging sessions.
The popular EV roaming protocols are:
- Open Charge Point Interface (OCPI),
- Open InterCharge Protocol (OICP),
- Open Clearing House Protocol (OCHP),
- eMobility Inter-operation Protocol (eMIP).
Open Charge Point Interface (OCPI)
The Open Charge Point Interface protocol (OCPI) is managed by the EVRoaming Foundation. This protocol is free to use and independent. It can work both bilateral as well as in combination with roaming hubs. While OCPI originated in Netherlands, you can find OCPI-based providers and operators in many countries including (but not limited to): Austria, Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Germany, India, Italy, Luxembourg, Poland, UK, Spain, South Africa, USA etc.
OCPI focuses on real-time communication between charge point operators. Its advantage lies in its simplicity, making it easy to implement and allowing for dynamic pricing and seamless roaming. The latest version to date is OCPI 2.2.1.
Open InterCharge Protocol (OICP)
The Open Intercharge Protocol (OICP) has been developed by Hubject, a group of German automotive and energy companies, in 2012. While other features are similar to OCPI, Hubject also acts as a hub and hence once a company is connected to the Hubject platform, it becomes open for integration with any other company already on the platform. The latest version to date is OICP 2.3.
Along with OCPI, OICP is one of the two roaming protocols that facilitates the exchange of signed meter data that confirms the amount of electricity provided to an EV during charging. OICP emphasizes data exchange and offers a comprehensive set of functionalities. Its advantage lies in its extensibility, enabling various business models and diverse charging networks to collaborate effectively.
Open Clearing House Protocol (OCHP)
The Open Clearing House Protocol (OCHP) was developed by SmartLab Innovationsgesellschaft GmbH and ElaadNL. The ev roaming protocol is managed by the roaming hub e-clearing.net. OCHP centers around a centralized clearinghouse for transaction data. Its advantage is in its security, ensuring secure data transfer and trusted transactions between charging networks.
Conventionally, OHCP supports hub-based roaming, however, there is also an extension named OCHP-direct that supports for peer-to-peer communication. The latest version to date is OCHP 1.4.
eMobility Inter-operation Protocol (eMIP)
eMIP is an EV roaming protocol that enables communication between MSPs and CPOs via a roaming hub. The eMIP specifications were designed and managed by GIREVE, which was founded by EDF, Renault, CNR and Caisse des Dépôts and other French companies. It is most widely used in France.
eMIP is the only protocol that supports a charge point search module, which allows EMSPs to retrieve a list of charge points located in a given geographic area based on a filter criteria like connector type etc. Further, eMIP brings together energy and mobility sectors. Its advantage is in its holistic approach, facilitating smart charging, renewable energy integration, and grid optimization, contributing to a sustainable EV ecosystem.
EMIP supports both roaming via the GIREVE platform and peer-to-peer connections. The latest version to date is eMIP 1.0.14.
The Differences between various EV Roaming Protocols
The table below highlights the main differences between various EV Roaming Protocols:
| Features | OCPI | OICP | OCHP | eMIP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P2P roaming | ✔ | ✔ | ||
| Hub roaming | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Charge Point Information | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Authorising charge sessions | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Remote Start/Stop Transcations | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Reservations | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Smart charging support | ✔ | |||
| Billing | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Communication | JSON/RESTful API | SOAP and JSON/RESTful API | SOAP | SOAP |
| Frequency | Real-time | Real-time | Asynchronous | Real-time |
Conclusion
As EV adoption accelerates, the collaboration between charging networks becomes crucial. The diverse EV roaming protocols cater to different needs within the evolving EV landscape. By fostering interoperability, these protocols lay the foundation for a convenient and accessible charging experience, accelerating the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable transportation future.