The Different Types of Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles or EVs are the type of vehicles that are partially or fully powered by electric power. The provide the advantage of zero emissions, eco-friendly, low running and maintenance costs etc. Electric vehicles are the key to sustainable transport. Let us discuss the types of electric vehicles.
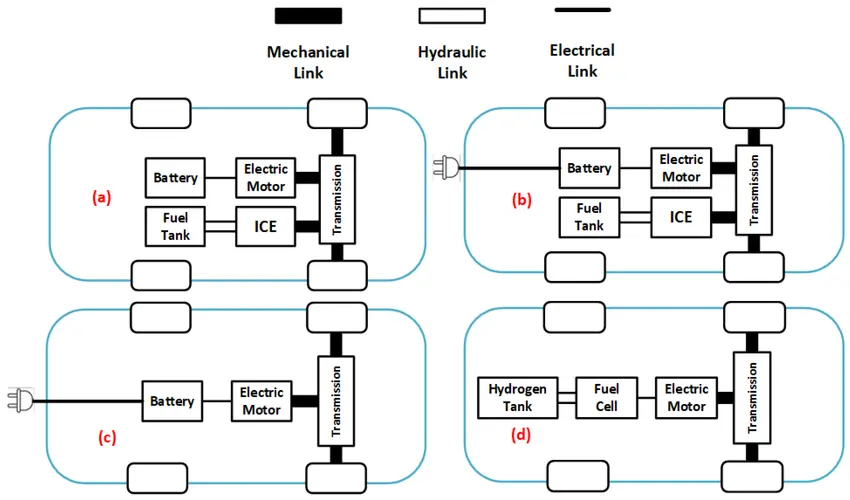
The classification is based on the type of mechanism used for energy production. The types of electric vehicles are :
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle(FCEV)
1. Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
In Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) all the energy required to run the electric motor comes from the battery pack. Use of gasoline is absent. Therefore, they emit zero emissions and are eco-friendly. They do not need a reduction gearbox. The battery can be charged from 10% to 80% in around 30 minutes with DC fast charging.
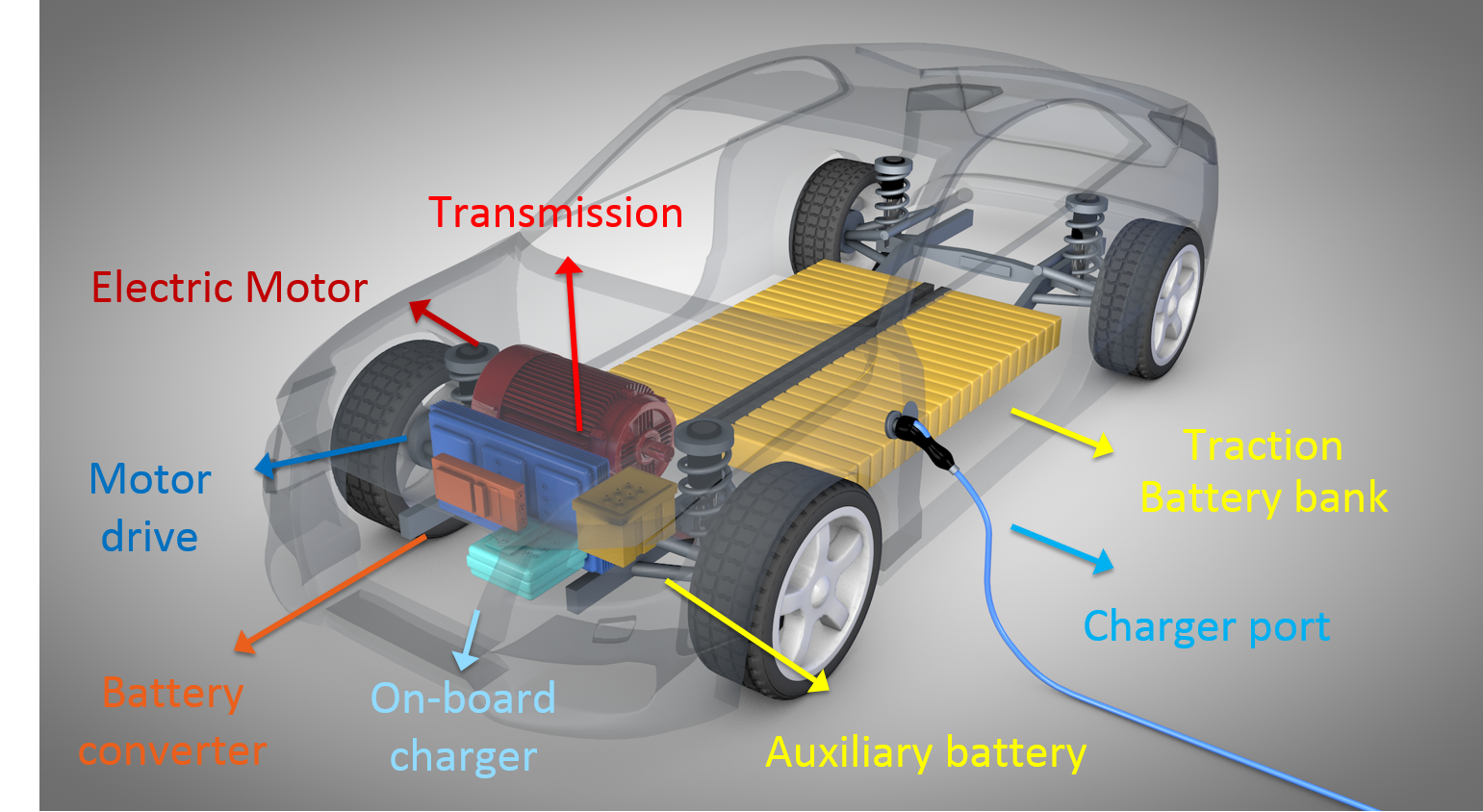
Key Features of BEVs
- BEVs have zero tailpipe emissions, making them the most environmentally friendly option.
- They are powered entirely by electricity, so regular charging is required.
- BEVs often offer a higher range with advanced models providing over 300 miles per charge.
- Popular BEVs include Tesla Model 3, Nissan Leaf, and Chevrolet Bolt.
Advantages of BEVs
- Zero emissions during operation.
- Lower maintenance costs as they have fewer moving parts.
- Quiet and smooth driving experience.
Challenges of BEVs
- Limited range compared to gasoline-powered vehicles (though improving).
- Charging infrastructure still needs to expand in some areas.
- Longer refueling times compared to traditional vehicles.
Battery Electric Vehicles are ideal for individuals looking for a fully electric solution, especially those living in urban areas with easy access to charging stations. They are a perfect choice for people committed to reducing their carbon footprint.
Examples : Tesla Model 3, Nissan Leaf, TATA Nexon, Mahindra E20 plus, MG ZS, Hyundai Kona, Mahindra eVerito etc.
2. Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV) consists of an engine and a motor. Fuel provides energy to the engine. Battery is the power source of motor. Regenerative braking and IC engine charges the battery. In addition, the battery cannot be charged by plugging in. They provide better fuel efficiency.
HEVs can be either Series or Parallel.

Key Features of HEVs
- HEVs use both gasoline and electric power, switching between the two for optimal efficiency.
- They do not require plugging in as they recharge through regenerative braking.
- Popular HEVs include the Toyota Prius, Honda Insight, and Hyundai Sonata Hybrid.
Advantages of HEVs
- Increased fuel efficiency compared to traditional gasoline vehicles.
- Lower emissions, especially in stop-and-go city driving.
- No need to worry about charging stations.
Challenges of HEVs
- Still rely heavily on gasoline, making them less eco-friendly than BEVs and PHEVs.
- Limited electric-only driving range.
- Higher initial cost compared to non-hybrid vehicles.
For drivers who want better fuel efficiency but aren’t ready for a fully electric vehicle, HEVs offer a middle-ground solution. These types of electric vehicles are ideal for those who want to reduce fuel consumption without changing their driving habits.
Examples : Chevrolet Tahoe Hybrid, Camry Hybrid, Lexus NX, Toyota Camry etc.
Read More
3. Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
Plug-in Hybrid Vehicle (PHEV) uses an on-board charger and a gasoline tank. The battery can be charged using regenerative braking or external plug-in. Furthermore, PHEV or Series Hybrid switches between electric and gas power. Since, PHEV uses smaller engines, it gives better performance.

Key Features of PHEVs
- PHEVs can run on electricity for a limited range (usually around 20-40 miles).
- Once the battery is depleted, the gasoline engine takes over, providing extended range.
- They can be plugged in to recharge the electric battery, similar to BEVs.
- Popular PHEVs include the Toyota Prius Prime, Ford Escape Plug-in Hybrid, and Volvo XC90 Recharge.
Advantages of PHEVs
- Flexibility of both electric and gasoline power.
- Reduced emissions compared to traditional vehicles.
- No “range anxiety” as the gasoline engine offers extended driving range.
Challenges of PHEVs
- Still emit some pollutants due to the gasoline engine.
- More complex systems mean slightly higher maintenance than BEVs.
- May require frequent recharging to maximize electric-only mode benefits.
PHEVs are a great option for those who want to experience electric driving but are not yet ready to fully rely on charging infrastructure. With their gasoline engine backup, these types of electric vehicles offer flexibility for both city driving and long trips.
Examples : Chevy Volt ,Ford C-MAX Energi, Hyundai Sonata, Chevy Volt etc.
Extended-Range Electric Vehicles (EREVs)
Extended-Range Electric Vehicles (EREVs) are another subtype to PHEVs but offer a longer electric-only range. They use an electric battery for propulsion but have a small gasoline engine as a backup. However, the gasoline engine does not directly power the vehicle; it only charges the battery.
Key Features of EREVs
- EREVs offer extended electric-only driving, usually between 40-80 miles.
- Once the battery is depleted, the gasoline engine recharges it.
- Popular EREVs include the Chevrolet Volt.
Advantages of EREVs
- Longer electric-only range compared to PHEVs.
- No range anxiety as the gasoline engine charges the battery.
- Reduced emissions compared to traditional vehicles.
Challenges of EREVs
- More complex than BEVs, leading to higher maintenance costs.
- Still rely on gasoline for longer trips.
- Limited availability of models compared to other electric vehicle types.
EREVs are ideal for those who want to maximize electric driving but still need the reassurance of gasoline backup for longer trips.
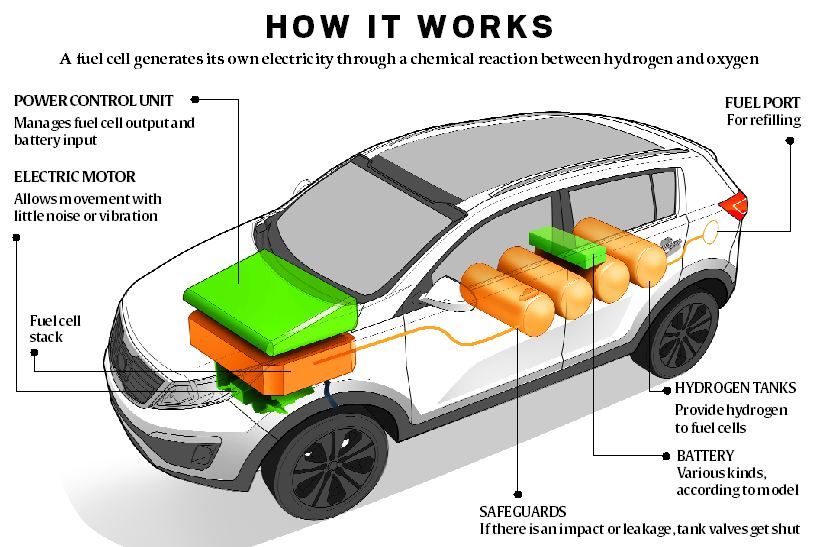
4. Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle(FCEV)
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV) are powered from the hydrogen. They emit zero emissions. In addition, they emit only water vapor and warm air. They are the least common electric vehicle. Hydrogen tank acts as a source of chemical energy. Furthermore, conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy happens. It takes about 10 mins to refuel the hydrogen tank. However the cost of FCEV is very high.
Key Features of FCEVs
- FCEVs use hydrogen as fuel and emit only water vapor.
- They have a longer driving range compared to BEVs, often over 300 miles.
- Popular FCEVs include the Toyota Mirai and Hyundai Nexo.
Advantages of FCEVs
- Zero emissions, only water is released as a byproduct.
- Faster refueling times compared to BEVs.
- Long driving range suitable for long-distance travel.
Challenges of FCEVs
- Hydrogen refueling infrastructure is still very limited.
- Producing hydrogen in an environmentally friendly way is still a challenge.
- Higher upfront costs compared to other electric vehicle types.
FCEVs represent a promising future for zero-emission transportation but are still in the early stages of widespread adoption. They are perfect for eco-conscious drivers in areas where hydrogen refueling stations are available.
Related article
Examples : Toyota Mirai, Hyundai Nexo, Riversimple Rasa, Hyundai Tucson FCEV etc.
Read Also
Comparison of types of electric vehicles
| BEV | HEV | PHEV | FCEV | |
| Presence of IC engine | IC engine is absent | Consists of both IC engine and electric motor. | Consists of both IC engine and electric motor. | Consists of both IC engine and electric motor. |
| Source of power | Electricity | Electricity and gasoline | Electricity and gasoline | Hydrogen tank |
| CO2 emissions | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| External Plug-in | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Stations for charging | Charging stations | Gas stations | Gas stations, charging stations | Gas stations |
Clean Machines: The 12 ‘Greenest’ Cars For 2021
How to Set up EV Charging Station | EV Charging Software | White Label EV Charging Software
Related article
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Electric Vehicle Type
When exploring the types of electric vehicles, it’s essential to consider your driving needs, environmental goals, and available infrastructure. Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) are perfect for those seeking a zero-emission lifestyle, while Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) offer flexibility for both short electric drives and longer trips.
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) provide improved fuel efficiency without the need for charging, and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs) represent a future with hydrogen-powered cars. Extended-Range Electric Vehicles (EREVs) strike a balance between electric driving and gasoline backup.
By understanding these electric vehicle types, you can choose the right EV that fits your lifestyle, contributes to sustainability, and meets your transportation needs. The future of transportation is electric, and with the right choice, you can be part of this exciting journey.