In the year 2024, the Electric Vehicles market is poised for remarkable growth, with projected global revenues reaching an impressive US$623.3 billion. This projection sets the stage for a promising future as the market anticipates sustaining a steady annual growth rate, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 9.82%(2024 – 2028). Two key entities in this ecosystem are Charging Point Operators (CPOs) and e-Mobility Service Providers (eMSPs).
While their names may sound similar, they play distinct roles in the growth of the EV charging infrastructure and eventually the EV ecosystem. In this blog, we will delve deeply into difference between CPO and eMSP.
Who is a CPO?
A Charging Point Operator (CPO) is a pivotal entity responsible for managing and operating charging stations for electric vehicles. CPOs are involved in the deployment, maintenance, and management of physical charging infrastructure. Their focus is on ensuring that charging stations are installed at strategic locations, providing EV users with convenient access to charging facilities.
CPOs are essential for building a robust charging network, collaborating with property owners, and handling the technical aspects of charging stations. They play a crucial role in expanding the charging infrastructure to meet the growing demand for electric mobility.
Who is an eMSP?
An e-Mobility Service Provider (eMSP) operates on a broader scale, offering services that go beyond the physical charging infrastructure. eMSPs focus on providing a seamless and user-friendly experience for EV owners. Their services often include charging station discovery, payment processing, and access to a network of charging stations.
eMSPs act as intermediaries between CPOs and end-users, simplifying the user experience by offering a unified platform for accessing multiple charging networks. They may provide mobile apps or RFID based Smart cards that grant EV users access to charging stations, making it more convenient for them to find, use, and pay for charging services
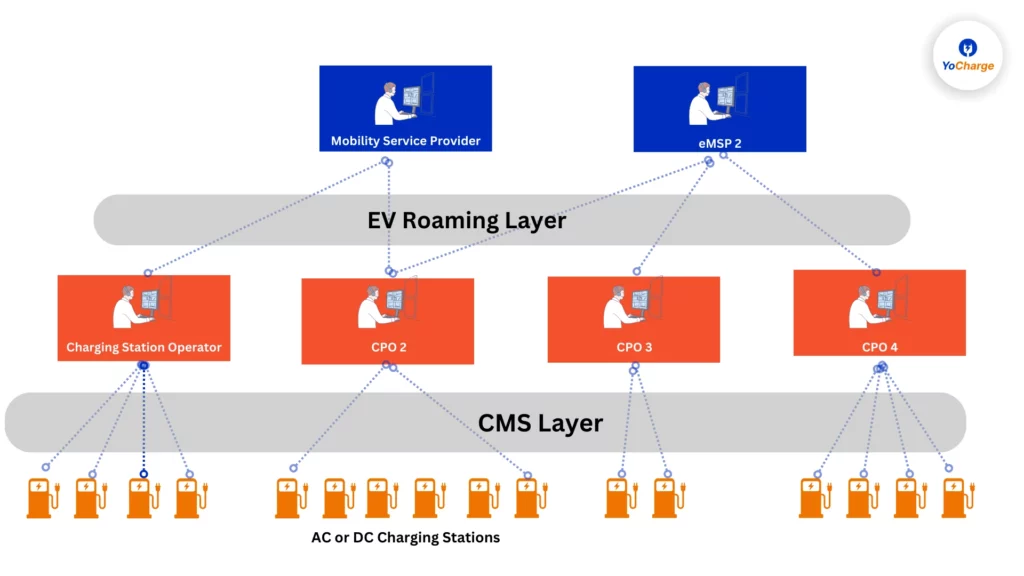
Electric Vehicle (EV) Roaming in the EV Charging Ecosystem:
In the electric vehicle (EV) charging ecosystem, EV roaming is the capability that allows electric vehicles to access charging stations operated by different Charge Point Operators (CPOs) through a standardized and seamless process. This ensures interoperability and enables EV drivers to utilize charging infrastructure across various networks without the need for multiple memberships or access cards.
Key Components of EV Roaming Ecosystem:
EV Roaming Layer:
The EV Roaming Layer serves as a pivotal component facilitating communication and interoperability between diverse Charge Point Operators (CPOs) and e-Mobility Service Providers (eMSPs). This layer operates through standardized protocols and communication interfaces, enabling the seamless exchange of information. Through these protocols, CPOs and e-MSPs communicate crucial details like charging station availability, session initiation, and authorization, ensuring a hassle-free user experience.
The utilization of standardized processes ensures that users can effortlessly initiate and authorize charging sessions across different networks, promoting a seamless and user-friendly cross-network charging access without complications.
CMS Layer (Clearing House Management System):
In the EV roaming ecosystem, the CMS Layer serves as a central hub, functioning as a clearinghouse for managing financial transactions and settlements among stakeholders. It consolidates charging session data by aggregating information from various Charge Point Operators (CPOs). The communication process between layers involves the aggregation of charging session data within the CMS Layer.
Subsequently, financial transactions, which include billing and reimbursement, are processed transparently through the CMS. This ensures a high level of accuracy and security in handling the financial aspects of EV roaming, contributing to the overall efficiency and reliability of the ecosystem.
Difference between CPO and eMSP
1. Scope of Operations:
CPO: Charging Point Operators primarily focus on the physical aspects of the charging infrastructure. Their responsibilities include the deployment, maintenance, and technical management of charging stations. CPOs collaborate with property owners, manage grid connections, and ensure the reliability of the charging infrastructure.
eMSP: On the other hand, e-Mobility Service Providers operate on a broader scale. They are not limited to the physical infrastructure but aim to provide a comprehensive service ecosystem. eMSPs offer services that extend beyond the boundaries of a single charging network, catering to the overall user experience in the electric mobility space.
2. Focus Area:
CPO: The primary focus of a CPO is on the technical and physical aspects of charging stations. This involves selecting suitable locations, installing and maintaining the charging equipment, and ensuring the stations’ seamless integration with the power grid.
eMSP: e-Mobility Service Providers prioritize user experience. Their focus is on creating a seamless and user-friendly interface for EV owners. This includes developing mobile applications, RFID cards, or other means to facilitate easy access, payment, and interaction with a network of charging stations.
3. User Interaction:
CPO: Charging Point Operators have limited direct interaction with end-users. Their primary stakeholders are property owners, municipalities, and other entities involved in the deployment of physical charging infrastructure.
eMSP: e-Mobility Service Providers directly interact with end-users. They serve as intermediaries, providing a user-friendly platform for EV owners to discover, access, and pay for charging services. This direct engagement enhances the overall user experience.
4. Services Offered:
CPO: CPOs are primarily involved in the deployment, maintenance, and technical management of charging stations. Their services revolve around ensuring the physical infrastructure is operational and reliable.
eMSP: e-Mobility Service Providers offer a broader array of services. In addition to charging station discovery, they facilitate payment processing and provide access to a network of charging stations operated by different CPOs. This integrated approach simplifies the user experience and encourages the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
| Criteria | CPO | eMSP |
| Scope of Operations | Physical charging infrastructure | Charging station discovery, payment processing, access to networks |
| Focus Area | Technical and physical aspects | User experience and convenience |
| User Interaction | Limited | Direct interaction with end-users |
| Services Offered | Infrastructure deployment | Charging station discovery, payment processing, network access |
Can a CPO also be an EMSP?
In some cases, a company or entity may choose to function as both a CPO and an eMSP. This integration allows them to provide end-to-end solutions, managing both the physical charging infrastructure and the user experience. This dual role can contribute to a more comprehensive and streamlined approach in the electric vehicle charging ecosystem.
Conclusion
In the evolving landscape of electric mobility, the collaboration and synergy between CPOs and eMSPs will play a pivotal role in shaping a sustainable and user-friendly future for electric vehicles. As the market continues to grow, innovations and integrations will likely further enhance the efficiency and convenience of EV charging systems. YoCharge, stands out as a prominent eMSP enabler in this landscape, providing comprehensive White-labelled eMSP platform solutions to give a better EV charging experience.
Want to learn more about how YoCharge can help your EV Charging business? Feel free to get in touch with us.
Get Started
Book Your Demo & get White-label solutions from our experts
or



