What is an EV Charger ?
Different types of EV Charger
One of the biggest concerns with Electric Vehicle owners is to know when and how to charge their vehicles. Despite electric vehicles taking the automobile world by storm, many challenges stop people from welcoming this change. We are used to driving around gas-powered cars and vehicles. Charging an electric vehicle is quite different and requires more planning. Growing demand and incentives for the charging stations have geared the demand and is now becoming more common than ever.
What is an EV charger ?
An EV charger is a equipment to keep the battery full for both electric vehicles and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. Just like any other charging device, EV Chargers help charge batteries of electric vehicles. In simple terms, when your mobile phone or laptop runs ut of battery, you search for a socket and plug-in a charger (adapter) connecting your mobile phone/laptop with the socket. The charger(adapter) converts & conditions electric power (mostly alternating) to DC power ( with required voltage) and charges the device.
In similar fashion, EV charger use electricity from grid (socket) and help charge batteries of your electric vehicle.
What are the various types of EV Charger ?
Well, EV chargers can be differentiated in multiple terms based on different parameters like location, charging speed, charging technology etc.
Types of EV Charger based on Output Current:
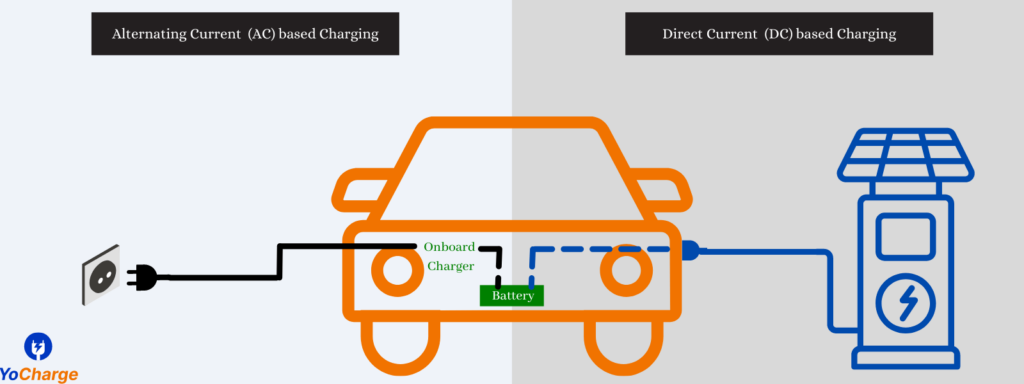
- AC Chargers: The AC EV Chargers take input AC current & provide AC output current. The ac current output from these chargers goes into the input of onboard charge controller (OBC) of electric vehicle which converts this ac current to dc current and feeds it to the battery. The ac chargers offer utility in terms of smart operation & metering, data analytics, safety, earthing & other checks etc.
- DC Chargers: The DC EV chargers take input of single or three phase AC current & provide output DC current. The output from these DC chargers bypasses the onboard charge controller and is directly fed into the battery.
Types of EV Charger based on location:
- Destination Chargers: Chargers installed on places like residential buildings, malls, hotels, offices etc. These are normally low voltage (240/415 Volts) AC Chargers.
- On the Go Chargers: Chargers installed on places like fuel pumps, highways, restaurants where EV users come, stop for a while, charge their vehicles and go. These are usually high voltage, DC Fast Chargers than can charge in short duration.
Types of EV Charger based on type of Hosts:
Charging stations come in two categories – Residential and commercial.
- Residential charging stations are meant for single-family houses. They may not have features like user authentication, scan & pay etc. Residential charging stations can be purchased.
- Commercial stations are much more advanced and have more hardware and software to operate. It is built in places around malls, offices and stores. It usually has more capacity and is also equipped with smart technology to manage the usage, scan and pay etc.
Types of EV Charger based on Power Ratings:
Usually, there are three main levels of charging an electric vehicle
- Level 1 – It is a very basic, standard charge of 240 VAC for an electric vehicle and takes much longer to charge.
- Level 2 – Also known as residential charging level, The energy is pushed to 240 Volts and 30 Amps. This energy is equal to the home washer and dryer.
- Level 2 (commercial) – When charging automobiles away from home, Level II commercial stations have become the industry standard. They provide the same 240V and 30 Amps as the domestic stations, but when the commercial networks are intelligent, the actual benefit is realised.
- Level 3 (DC fast charging) – Level III, also known as DC Fast Charging, uses a voltage range of 200 to 600 VDC to refill an electric car in as short as 30 minutes. This is an excellent option for on-the-go charging.
An EV may be charged in three different ways. A typical Level 1 domestic wall socket may be used to charge the car. You may connect the car to a Level 2 home charging station, which utilises a higher-capacity 240-volt outlet, comparable to what certain household appliances require. Alternatively, you may use a Level 2 or Level 3 public charging station.
Unlike a smartphone, which can be charged by plugging it into any normal wall socket because all gadget makers use the same plug, EVs have their own set of connections. When using a public charging station, you must first determine which type of charger is compatible with your car.
Read in detail
EV Chargers based on Portability
- Portable EV Chargers: Portable EV Charger are chargers that are not fixed and can be taken along with the electric vehicle. Usually, these chargers are supplied complimentary by ev manufacturers while you purchase the vehicle. Portable ev charger connects to domestic 6A or 16 A sockets and can be used for charging the electric vehicles without any upgradation of electric infrastructure. Consequently, these are slow chargers and charge the ev’s at very low speed.
- Fixed EV Chargers: Most of chargers that used for electric vehicle charging are of fixed type only. These chargers are installed at particular location and electric vehicles come to the location & use the chargers. Again, based on how chargers are installed, these chargers can be further divided into wall-mounted or ground mounted chargers.
Introducing YoCharge
YoCharge provides EV Charger Software Solutions for all types of use cases. If you are looking for EV Charging software & mobile apps, you should contact our team.
YoCharge software connects with any company EV Charger & helps you control that charger remotely through mobile application.